-
Posts
1948 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by Spyman
-

Why doesn't the space curvature restore the path of a photon?
Spyman replied to Lazarus's topic in Astronomy and Cosmology
If you made a depression in a pool table, like in the image krash661 presented in post #5, a billiard ball placed where the "earth" is and rolled towards the "percieved position of star" wouldn't follow the red line or any other grid lines painted on the surface, instead the curved surface would bend the path such as the yellow line shows, towards the "actual position of star". The grid lines are only there to help us see the shape of the cavity, they do not represent the course of passing objects through the depression, as Janus points out in his post #6. Two-dimensional analogy of spacetime distortion generated by the mass of an object. Matter changes the geometry of spacetime, this (curved) geometry being interpreted as gravity. White lines do not represent the curvature of space but instead represent the coordinate system imposed on the curved spacetime, which would be rectilinear in a flat spacetime. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitation -
The Big Bang was not an explosion throwing matter outward to fill an empty void.
-
Adding to what ACG52 and MigL already have said above, the expansion of the Universe is no longer thought to be decelerating either, gravity managed to slow down the expansion during the first ~8 billion years but then the rate of expansion started to increase. The 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics were awarded to Saul Perlmutter, Brian P. Schmidt, and Adam G. Riess for the discovery of the accelerating expansion. Dark energy is now the most accepted hypothesis to explain the accelerated expansion. In 1998, cosmology was shaken at its foundations as two research teams presented their findings. Headed by Saul Perlmutter, one of the teams had set to work in 1988. Brian Schmidt headed another team, launched at the end of 1994, where Adam Riess was to play a crucial role. /../ For almost a century, the Universe has been known to be expanding as a consequence of the Big Bang about 14 billion years ago. However, the discovery that this expansion is accelerating is astounding. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/2011/press.html In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted hypothesis to explain observations since the 1990s that indicate that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. In the standard model of cosmology, dark energy currently accounts for 73% of the total massenergy of the universe. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dark_energy Cosmologists estimate that the acceleration began roughly 5 billion years ago. Before that, it is thought that the expansion was decelerating, due to the attractive influence of dark matter and baryons. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dark_energy
-
SPEEDING BLACK HOLE A nearby black hole, hurtling like a cannonball through the plane of our Milky Way, has provided possibly the best evidence yet that stellar-mass black holes are made in supernova explosions. This black hole is streaking through space at a rate of 400 000 kilometres per hour - four times faster than the average velocity of the stars in the galactic neighbourhood. What has made it move so fast? The most likely 'cannon' is the explosive kick of a supernova, one of the Universe's most titanic events. http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/Speeding_black_hole The runaway black hole GRO J1655-40 Abstract. We have used the Hubble Space Telescope to measure the motion in the sky and compute the galactocentric orbit of the black hole X-ray binary GRO J1655-40. The system moves with a runaway space velocity of 112±18 km s−1 in a highly eccentric (e = 0.34 ±0.05) orbit. The black hole was formed in the disk at a distance greater than 3 kpc from the Galactic centre and must have been shot to such eccentric orbit by the explosion of the progenitor star. The runaway linear momentum and kinetic energy of this black hole binary are comparable to those of solitary neutron stars and millisecond pulsars. GRO J1655-40 is the first black hole for which there is evidence for a runaway motion imparted by a natal kick in a supernova explosion. http://arxiv.org/pdf/astro-ph/0211445.pdf
-

The Final Frontier: Achievable in high school?
Spyman replied to tibieuh's topic in Astronomy and Cosmology
Depending on ambition, balloons seems to be a cheap option. Out of this world! Student takes stunning snaps of space using only a £30 second- hand camera and a balloon Device costing £200 launched by Worcestershire teenager Adam Cudworth Spent 40 hours working on box with GPS tracker, radio & microprocessor Located device after fall back to earth having reached speeds of 150mph Spectacular: The images look like they could be the latest taken from a multi-million pound NASA satellite http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2200559/Adam-Cudworth-Student-takes-stunning-snaps-space-using-30-second-hand-camera-balloon.html -
Rogue planets are very hard to detect which causes a large range of estimations upwards to a very high number of free-floating planets for every star in the Milky Way. But even if they are more or less everywhere, Jupiter sized planets only contain a fraction of the mass of a normal star, (from one thousandth up to one hundredth of the Sun), and thus needs to come much closer to disturb the Oort cloud. Observation When a planetary-sized object passes in front of a background star, its gravitational field causes a momentary increase in the visible brightness of the background star. This is known as microlensing. Astrophysicist Takahiro Sumi of Osaka University in Japan and colleagues, who form the Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics (MOA) and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE) collaborations, carried out a study of microlensing which they published in 2011. They observed 50 million stars in our galaxy using the 1.8 meter MOA-II telescope at New Zealand's Mount John Observatory and the 1.3 meter University of Warsaw telescope at Chile's Las Campanas Observatory. They found 474 incidents of microlensing, just 10 of which were brief enough to be planets of around Jupiter's size with no associated star in the immediate vicinity. The researchers estimated from their observations that there are nearly two free-floaters for every star in our galaxy. Other estimations suggest a much larger number, up to 100,000 times more free-floating planets than stars in our Milky Way. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rogue_planet#Observation Planetary-mass objects A planetary-mass object, PMO, or planemo is a celestial object with a mass that falls within the range of the definition of a planet: massive enough to achieve hydrostatic equilibrium (to be rounded under its own gravity), but not enough to sustain core fusion like a star. By definition, all planets are planetary-mass objects, but the purpose of the term is to describe objects which do not conform to typical expectations for a planet. These include dwarf planets, the larger moons, free-floating planets not orbiting a star, such as rogue planets ejected from their system, and objects that formed through cloud-collapse rather than accretion (sometimes called sub-brown dwarfs). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planetary-mass_object#Planetary-mass_objects Brown dwarfs are substellar objects too low in mass to sustain hydrogen-1 fusion reactions in their cores, unlike main-sequence stars, which can. They occupy the mass range between the heaviest gas giants and the lightest stars, with an upper limit around 75 to 80 Jupiter masses (MJ). Brown dwarfs heavier than about 13 MJ are thought to fuse deuterium and those above ~65 MJ, fuse lithium as well. However, for some years now there has been debate concerning what criterion to use for defining the separation between a brown dwarf and a giant planet at very low brown dwarf masses (~13 Jupiter masses). One school of thought is based on formation, and another on interior physics. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brown_dwarf A sub-brown dwarf is an astronomical object formed in the same manner as stars and brown dwarfs (i.e. through the collapse of a gas cloud) but that has a mass below the limiting mass for thermonuclear fusion of deuterium (about 13 Jupiter masses) and that hence is not a brown dwarf. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sub-brown_dwarf Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in the Solar System combined. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter
-
Sounds more and more as Bart's old thread: Gravitational time dilation, where he argues that such synchronized clocks will rule over all physical events on the spaceship. But events and happenings on a fast spaceship will not unfold in accordance with such a clock, they will take place on a timescale of the local time.
-
But we can measure the redshift in the light from nearby stars and conclude that they are moving away or towards us with different speeds which suggests that our Solar system and other stars are passing by each others, as they orbit in the Milky Way. We also have the ability to view other similar galaxies and model how stars behave in their large structure. It is somewhat unfair to say that we don't have evidence of any *passing stars* when we don't have been advanced long enough to be able to observe and record such an encounter. Below is a picture from Wikipedia that shows how, astronomers predict based on current knowledge and observations, the nearest stars will vary in distance over the next 80 thousand years. Future and past Ross 248, currently at a distance of 10.3 light-years, has a radial velocity of −81 km/s. In about 31,000 years it may be the closest star to the Sun for several millennia, with a minimum distance of 0.927 parsecs (3.02 light-years) in 36,000 years. Gliese 445, currently at a distance of 17.6 light-years, has a radial velocity of −119 km/s. In about 40,000 years it will be the closest star for a period of several thousand years. Distances of the nearest stars from 20,000 years ago until 80,000 years in the future http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_nearest_stars#Future_and_past In spiral galaxies, the spiral arms do have the shape of approximate logarithmic spirals, a pattern that can be theoretically shown to result from a disturbance in a uniformly rotating mass of stars. Like the stars, the spiral arms rotate around the center, but they do so with constant angular velocity. The spiral arms are thought to be areas of high-density matter, or "density waves". As stars move through an arm, the space velocity of each stellar system is modified by the gravitational force of the higher density. (The velocity returns to normal after the stars depart on the other side of the arm.) This effect is akin to a "wave" of slowdowns moving along a highway full of moving cars. The arms are visible because the high density facilitates star formation, and therefore they harbor many bright and young stars. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galaxy#Spirals Another interesting aspect is the so-called "wind-up problem" of the spiral arms. If the inner parts of the arms rotate faster than the outer part, then the galaxy will wind up so much that the spiral structure will be thinned out. But this is not what is observed in spiral galaxies; instead, astronomers propose that the spiral pattern is a density wave emanating from the Galactic Center. This can be likened to a moving traffic jam on a highway—the cars are all moving, but there is always a region of slow-moving cars. This model also agrees with enhanced star formation in or near spiral arms; the compressional waves increase the density of molecular hydrogen and protostars form as a result. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Milky_Way#Spiral_arms
-
1) Considering the recent close flyby of asteroid 2012 DA14 and the Chelyabinsk meteor blast, what is your opinion of future impact threats and deflection strategies? 2) What are your thoughts on SETI, are we alone in the Milky Way or do you think that we one day will establish radio contact with another technological civilization?
-
Dark matter and Dark energy are two entirely different phenomena! Dark matter is responsible for holding galaxies together even though they have a higher rotational velocity than what the gravity from visible matter can maintain. It is called "dark" because it is something yet unknown and it doesn't interact with light so we can't see it directly, not because it is colored black or have an opposite relationship with something else. Dark energy on the other hand is what's causing the accelerated expansion of the Universe, it is a force that overpowers gravity on very large distances and seems to push things apart. It is also named "dark" because we don't yet know what it consists of, which can cause confusion, but as with Dark matter the name is not linked to some kind of evil force or similar. White matter is some kind of brain tissue and is not a cosmological description or designation.
-
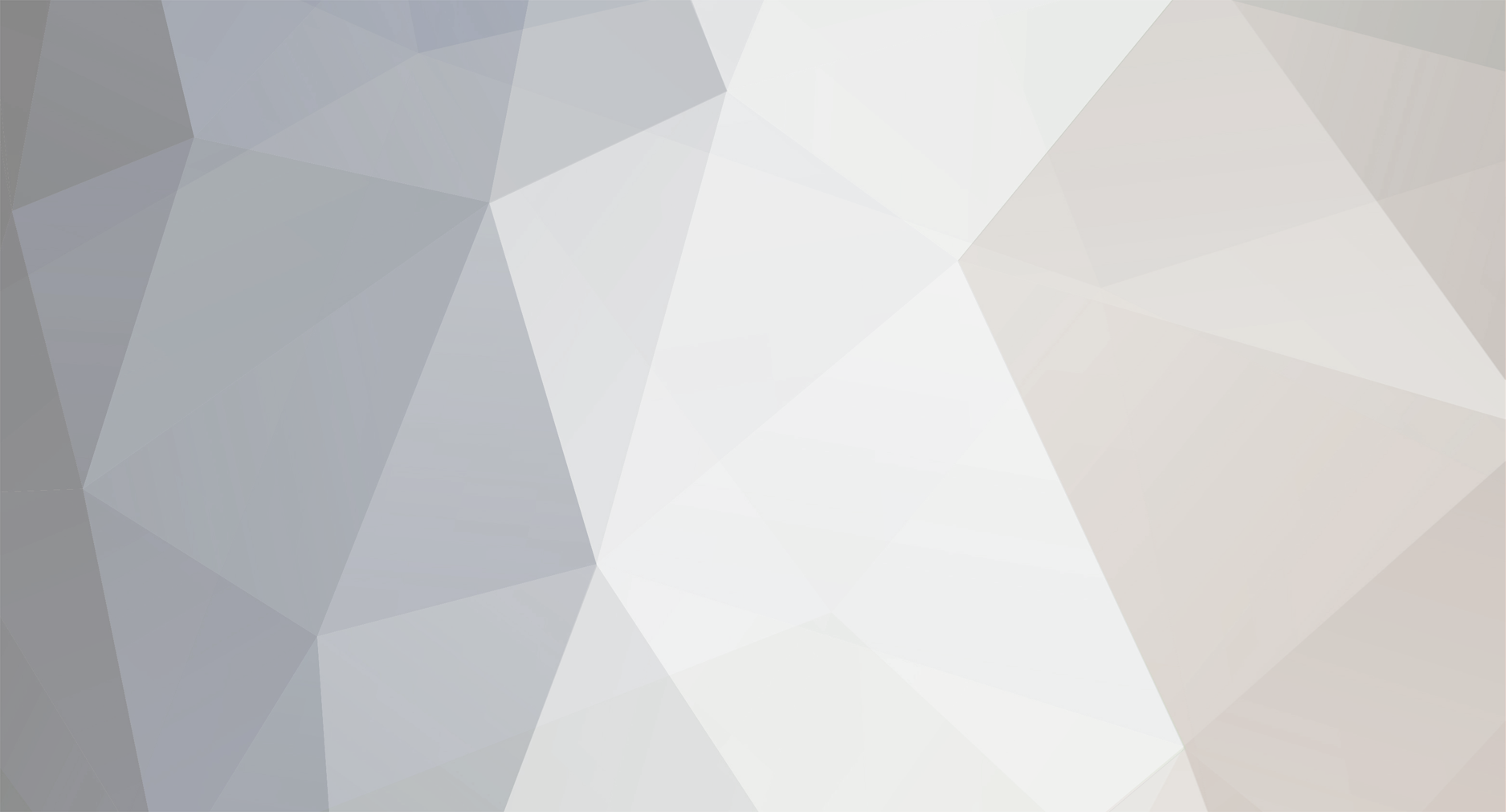
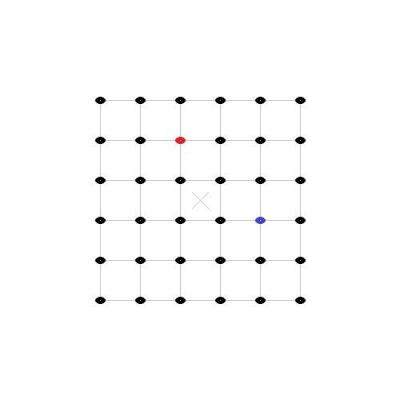
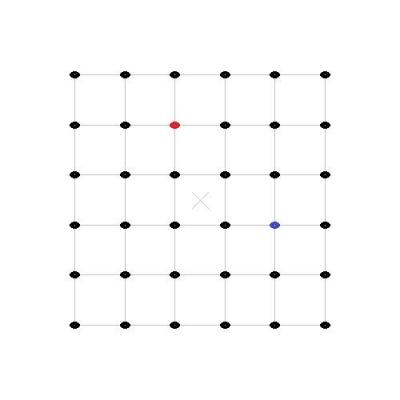
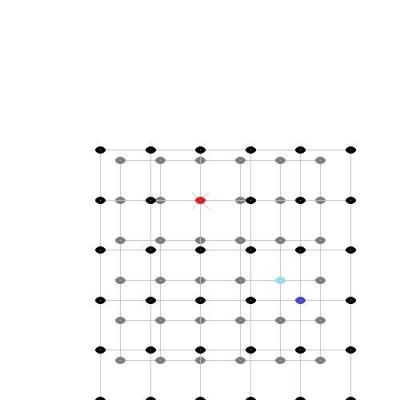
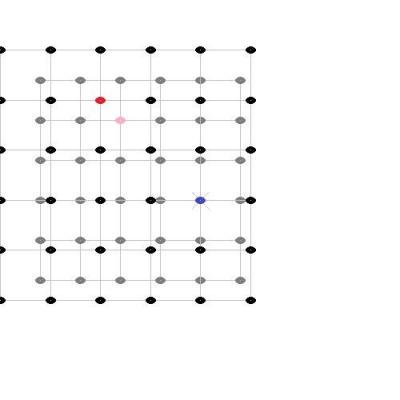
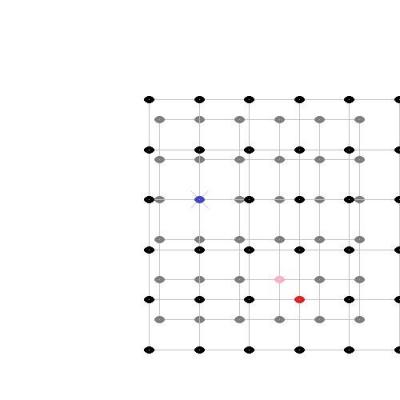
Actually my analogy did allow for several different locations of observations since the observer was moving around inside the building, while measuring distances with a ruler, so there was access to more than one view and I even included a meeting with another observer to compare results, but I think I understand your question better now - so let's try again. (I am not going to do this in full 3D, so I hope that this 2D visualization is enough.) Here are two images of evenly distributed objects, painted as black dots, but to distinguish two of them from the others, they have been colored red and blue. Space has been expanded by about a quarter between images: If I take those two images and put them above each others with the red dot in the center, to show how the red observers views the expansion, then it looks like this: And likewise, the same two images above each others but with the blue dot in the center, to show how the blue observers views the expansion, then it looks like this: Finally we can turn the image with the blue dot in the center around and place them next to each others, to show that their views are identical regarding space expansion:
-
alexro, try to imagine that you are in a very large building that has various objects spread out on the floor in a homogenous and isotropic pattern. You have a clock and a ruler that you use to measure and record distances between the objects on regular intervals. After several sets of measurements, you will notice that you, your ruler and all other objects inside the building appears to be shrinking, because all distances between each object increases at the same scalar way, over the duration of a certain time. You get worried and start making more accurate measurements, which reveal that the rate of change slowly increases with time. Next day when you meet up with another observer and compare measurements, you notice that while ranges and durations match, the other person thinks that it is the building that is growing and bringing the objects apart instead of objects shrinking. In Einstein's theory of general relativity the geometry of space is dynamic, it can expand or contract, and when applying this to cosmological models the scale of space in the Universe can change relative the observer's ruler, such that distances between objects can increase without actual movement. Acceleration means that the rate of expansion is speeding up with time and happens faster. Follow the link under the quote and you will find much more to read: "The metric expansion of space is the increase of the distance between two distant parts of the universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself is changed. That is, a metric expansion is defined by an increase in distance between parts of the universe even without those parts "moving" anywhere. This is not the same as any usual concept of motion, or any kind of expansion of objects "outward" into other "preexisting" space, or any kind of explosion of matter which is commonly experienced on earth." http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metric_expansion_of_space
-
Hi bascule and Welcome back! Since your old account still seem to be active, I think you should ask someone in the staff for help to retrieve it or if you explicitly want a fresh start tell them to lock it.
-
I am sorry, but your "basics" image does not help me understand why you think NASA's pictures are wrong and from your explanation in post #11, it still seems likely that you are misinterpreting them.
-
The asteroid flyby and Russian meteor explosion had significantly different trajectories, showing that they were completely unrelated events, NASA officials said. http://www.space.com/19838-russian-meteor-blast-bigger-size.html
-
Not only do you seem to claim that the consensus of mainstream science is wrong but also that professional cosmologists all over the world are unable to understand and properly use Newton's laws when they are applying them on rotating galaxies. IMHO, I think it would be wise for you to at least consider the possibility that it might be you that are wrong. This is a quote from the lecture your image is from: Surprisingly, the rotation curves that were measured even for a wide range of galaxy sizes and luminosities exhibited a nearly flat (and even slightly increasing) region of velocities outside the galactic center. If most of the galactic mass were at the center of the galaxy (which is the source of most of the luminosity), then one would expect the velocities of the outermost stars to decrease with increasing distance. This velocity dependence would be like the Keplerian dependence observed in planetary motion. The velocity of the outermost stars orbiting with uniform circular motion can easily be determined by equating the gravitational force of attraction to the galactic core with the stellar mass times the centripetal acceleration. The velocity can then be seen to fall off as one over the square root of the orbital radius, contrary to the measured, nearly flat, rotation curves. This provides further evidence for the possible existence of a large quantity of non-luminous galactic mass. Furthermore, these results suggest that much of this extra mass is farther from the galactic center than the luminous mass. http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2007/ph210/sugarbaker2/ Newton's laws of motion and gravity says that orbiting velocity should decrease with the square root of the orbital radius. Any "analytical tool" that uses a Newtonian method and disagrees with this is in dire need of error corrections. No, you are wrong - the consensus among mainstream science is very clear that the phenomenon exists and are real. According to consensus among cosmologists, dark matter is composed primarily of a not yet characterized type of subatomic particle. The search for this particle, by a variety of means, is one of the major efforts in particle physics today. Although the existence of dark matter is generally accepted by the mainstream scientific community, several alternative theories have been proposed to try to explain the anomalies for which dark matter is intended to account. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dark_matter The statement: "This is the most robust direct measurement of the local dark-matter density to date." is definitely not a doubtful comment and as has already been pointed out to you in post #2, the missing baryon problem is different from dark matter. Researchers think the mass inside this halo could be the answer to what's called the "missing baryon problem." http://www.space.com/17734-milky-way-galaxy-giant-gas-halo.html Baryons are a class of subatomic particles that includes the protons and neutrons that make up the atoms inside stars and galaxies. http://www.space.com/17734-milky-way-galaxy-giant-gas-halo.html This missing matter is not to be confused with dark matter, an exotic form of matter that can only be detected by its gravitational pull. http://www.space.com/5368-missing-cosmic-matter.html
-
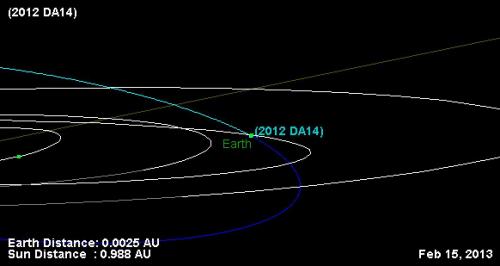
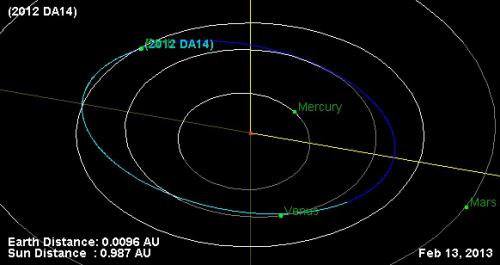
Like Ophiolite, I am also confused and unable to spot any errors made by NASA, but there is a small possibility that you could have misinterpreted their pictures in the link you presented in the OP. I suspect this because you have reversed the side elevation. This are the images on that page: Graphic depicts the trajectory of asteroid 2012 DA14 on Feb 15, 2013. In this view, we are looking down from above Earth's north pole. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech http://www.nasa.gov/topics/solarsystem/features/asteroidflyby.html Graphic depicts the trajectory of asteroid 2012 DA14 during its close approach, as seen edge-on to Earth's equatorial plane. The graphic demonstrates why the asteroid is invisible to northern hemisphere observers until just before close approach: it is approaching from "underneath" our planet. On the other hand, after close approach it will be favorably placed for observers in the northern hemisphere. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech http://www.nasa.gov/topics/solarsystem/features/asteroidflyby.html Please note that for some reason there is no arrow pointing towards the Sun in the second picture, which can make it seem like that image is viewed as seen from the Sun towards Earth, however in this picture from my link in post #2 there is an arrow pointing towards the Sun, which is to the left side of the image: Diagram showing Asteroid 2012 DA14's passage by the Earth on February 15, 2013. http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news177.html
-
Well, I don't think you have to worry, if NASA have asked Australian amateur astronomers to track the asteroid, then they are more than likely able to discover any mistakes and correct for them in time such that they don't miss the approach. Further more since the asteroid will approach from the South and recede to the North, the Goldstone observatory in California, the Haystack Observatory in Massachusetts and the EISCAT radar near Tromso in Norway will make radar observations during that part of the encounter.
-
LOL, copycat You said: "I don't think it will hit", which I clarified to avoid people getting scared. I don't understand your question, follow my link and by revolving and zooming further you can get this picture: Image obtained from: http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2012+DA14;orb=1 Which clearly shows that the asteroid goes in and out of Earths neighbourhood while still orbiting the Sun.
-
AFAIK, NASA is very confident that 2012 DA14 will NOT hit Earth and neither become a satellite thereof. 2012 DA14 orbits the Sun like Earth but in a slightly different orbit and while the close encounter will change the asteroids orbit from 368 days to 317 days, it will take more than 30 years before it will come close to Earth again. "The asteroid will not impact Earth on February 15, 2013." http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2012_DA14 "The 2013 close approach to Earth will reduce the orbital period of 2012 DA14 from 368 days to 317 days. The close approach to Earth will perturb the asteroid from the Apollo class to the Aten class of near-Earth asteroids. The next notable close approach to Earth will be on 15 February 2046 when the asteroid will pass no closer than 0.01 AU (1,500,000 km; 930,000 mi) from the center-point of Earth." http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2012_DA14 "NASA's NEO Program Office can accurately predict the asteroid's path with the observations obtained, and it is therefore known that there is no chance that the asteroid might be on a collision course with the Earth." http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news177.html "Since 2012 DA14's orbital period around the Sun has been about 368 days, which is very similar to the Earth's, the asteroid made a series of annual close approaches, this year's being the closest. But this encounter will shorten 2012 DA14's orbital period to about 317 days, changing its orbital class from Apollo to Aten, and its future close approaches will follow a different pattern. The close approach this year is the closest the asteroid will come for at least 3 decades. http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news177.html Image obtained from: http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2012+DA14;orb=1
-
To be fair, the Trash Can contains all kinds of crap from lots of subforums and even though most of them are likely from Speculations, there is no real need for Speculations to hold all the trash and if it would make Speculations to a more attractive and respected subforum then the Trash Can could be moved out of there to somewhere else, like beside The Sandbox under Suggestions, Comments and Support or have its own location all the way at the bottom. Also, if it would help people feel better about Speculations it could possibly be moved up to the top in Other Topics above The Lounge and other subforums there. I don't think anyone will complain that Politics is located to close to the Trash Can if Politics and Speculations should switch locations, but it would eliminate complaints that Speculations is placed next to the waste basket. However, since this site is intended as a *science* forum and not a *speculations* forum, I think it is obvious that mainstream science should be located above other topics and categories like speculations. This I strongly agree with. I think it is very important that speculations are clearly separated from established science so that people coming here to learn don't have any problem discerning facts from fiction, thus Speculations should not be named with something that can cause confusion with any category of mainstream science or be located under the same main forum which could give it a false credibility.
-
If the program "Sagitarius BR" has different results than mainstream science, then it must either use different methods or other estimates than what mainstream science does when they reach the consensus that the dark matter phenomen is real. IMHO, I don't think random simulations made by strangers on the internet that uses conflicting methods and estimates to end up with contradicting results against conclusions made by mainstream science to be very convincing at all. Claims that the consensus made by mainstream science are all wrong should be taken with a very large dose of skepticism! In fact as ACG52 points out in his post#3, observations made by astronomers confirm that dark matter is fully consistent with standard estimates: "This is the most robust direct measurement of the local dark-matter density to date." Observational evidence wins and it currently favors a dark matter phenomena as depicted by mainstream science.
-

Labeling units on the reputation system
Spyman replied to SamBridge's topic in Suggestions, Comments and Support
I enjoy the current freedom I have to vote up or down entirely on my personal judgement. If the voting system becomes limited or complicated, then I will likely stop using it. -
It think Moontanman ment that he would want to know if or how cathy's and others who come here have their problems solved. (And not about how we should deal with resurrection of old threads.) I agree with him, it would be nice to find out how it ended.
-
IF our Universe is a simulated reality program running inside a powerful computer, then a "Creator" could more than likely copy and run several identical programs or stop and restart one single program several times. Omniscience could then also be achieved by making the program deterministic and presetting the initial conditions or by regulary pausing the program and adjust the parameters before restarting from an earlier timestamp such that it continues on right track. The Simulation Argument: Why the Probability that You Are Living in a Matrix is Quite High