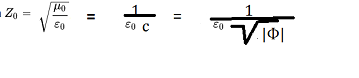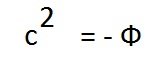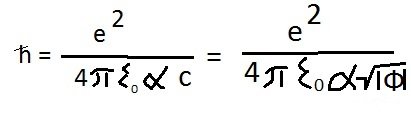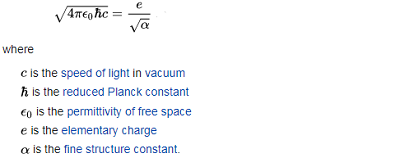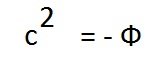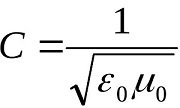SergUpstart
Senior Members-
Posts
501 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
1
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by SergUpstart
-
Astronomers have witnessed for the first time how a large star in one of the neighboring dwarf galaxies, located in the constellation Aquarius, suddenly disappeared from the sky, presumably directly turning into a black hole. This was announced on Tuesday by the press service of the European southern Observatory (ESO). "Such large stars usually produce bright supernova bursts at the end of their lives, which is why the disappearance of this star has become an extremely unusual event for us. If it really directly turned into a black hole, then we are the first direct witnesses of how the life of a giant star ended in such a manner," said Andrew Allan, an astrophysicist from Trinity College in Dublin (Ireland), whose words are quoted by the ESO press service. https://learningenglish.voanews.com/a/scientists-say-a-massive-star-has-mysteriously-disappeared/5485235.html#:~:text=Astronomers say a massive star,in the constellation of Aquarius.
-

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Yanchilin's equations are slightly different from Newton's Newton's Phi (r)=Gm/r g (r) = Gm/r^2 Yanchilin'sPhi(r)=2Gm/r g(r)=(dPhi/dr)/2=Gm/r^2 This reflects the law of conservation of energy. When an Apple accelerates when it falls from a height H, the energy of the Apple changes not by the amount of mgH, but by the amount of 2mgH. Half of that energy to change the kinetic energy mv^2/2, and the other half goes to the change in internal energiei that of Apple, which is Einstein's E=mc^2, and Yanchilin's respectively E=-mphi. A photon has a rest mass of 0, so all this energy is used to change the kinetic energy of the photon. 2mgH and not mgH, as in Newton. This explains and corrects the error Of Newton's theory, which predicts the deflection of a ray of light in a gravitational field exactly 2 times less than GRT. How are you going to measure local time and determine when to stop counting decay events? There's no way without a second watch. Have there been experiments with two different clocks? -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Let's go back to the clock experiment. The new theory States that as the gravitational potential increases, Planck's constant decreases, which should REDUCE the rate of radioactive decay. We need an experiment not with one, but with a couple of hours, where one will work on the principle of radioactive decay, and the other as a quantum frequency standard. This pair of hours is set at the top and synced, then we lower the pair of hours down and they will have to be out of sync. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Yes, you are right, such an experiment will help you find the truth -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Let's say we count 1000 pulses from the Geiger counter. In fact, we form a rectangular pulse, whose front front coincides with the first pulse, and the back - with the 1000th. when transmitting it to an external observer, we will get the same rectangular pulse, the duration of which will be formed by a proportional change in all the frequencies of its spectrum. Nothing will work, we check the gravitational frequency shift. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
The law of conservation of energy will not be violated, the rest masses of all bodies are also variable and are determined by the gravitational potential. Here I found a link to this theory in English https://vixra.org/pdf/1603.0398v1.pdf It is useless to accumulate impulses, this only narrows the Delta f. With a gravitational shift all frequencies of the spectrum will change by the same relative value -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Yanchilin assumed that the splitting of spectral lines in distant quasars will not change, so the constant of the fine structure does not change. He also showed that the variation of the elementary charge violates the law of conservation of energy. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Indeed, it is impossible to refute GRT using a formula . But not because the formula is incorrect, but because we can not fundamentally compare the course of the clock at points with different gravitational potential, bypassing GRT. And radioactive decay will not help here, since it is necessary to compare the number of decay events for and the time intervals for which they occurred, and it is impossible to compare these time intervals bypassing GRT. But to conduct this experiment with the measurement of the magnetic constant at different gravitational potentials would still be interesting, not from the point of view of checking GRT, but from the point of view of checking the above formula. In addition, a previously unknown effect can be detected, the dependence of the wave resistance of the vacuum on the gravitational potential -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Yanchilin considered two atoms that are at different heights above ground level, the height difference is equal to H, and emit photons at the same energy transition. the frequency of the photon emitted by the atom at point A (below) is higher by relative value 2gH/c^2 than the frequency of the photon emitted exactly the same atom at point B (above). But while the photon is flying up, its the frequency is lowered by a relative value of 3gH/c^2 . At the same time 2/3 this value (i.e. 2gH/c^2) is caused by a decrease in the photon energy (the energy of a photon decreases twice as fast as the energy of a non-relativistic body because the photon has no rest energy), and 1/3 of this values (i.e. gH/c^2) caused by an increase in the Planck constant. Thus, the total result of the two effects is that the frequency of the photon emitted by the atom below decreases when it rises to the height H by a relative value of gH/c^2, which coincides with the result predicted by GRO and corresponds to the experimental data. Agree that this explanation is simple, logical, and it is devoid of contradictions that exist in the explanation from the point of view of GR. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
It follows from the formula that the square of the speed of light is not an invariant, but depends on the gravitational potential. In addition, Yanchilin's theory contradicts GRT. According to GRT, time slows down near massive bodies, but in the Yanchilin's theory, it accelerates on the contrary, although due to the gravitational redshift, the remote observer has the illusion that time slows down near a massive body. It also follows from the formula written above that black holes do not exist, since the speed of light increases in proportion to the square root of the gravitational potential. Light can leave the vicinity of any massive body, but the amount of gravitational redshift is not limited. Theoretically, it is possible that leaving the vicinity of a sufficiently massive body, even gamma radiation can turn even into radio waves of the ultra-long-wave range -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
I wrote about this award not because I want to get it😃😃, but because they quite reasonably do not consider gravitational redshift to be proof of time slowing down near a large mass. It can be explained in another way. Moving away from a massive body, a photon with its own mass spends its energy on performing work against the force of gravity and its energy decreases, and therefore its frequency decreases. Their team believes that there is no other way to test the theory other than directly measuring the passage of time at different gravitational potentials using a very accurate atomic clock. I see another method based on a different physical principle. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
If they had measured not the strength of the magnetic field (which was 400 times weaker than expected) but the magnetic permeability of space, it would not have been a "possible interpretation" but a fait accompli. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Based on the law of Biot-savard-Laplace, the smaller the magnetic constant, the weaker will be the strength of the magnetic field created by a current of the same force. Briefly, the essence of Yanchilin's quantum theory of gravity theory, as it explains the mechanism of gravitational attraction. The square of the speed of light is equal to the gravitational potential with a minus sign Planck's constant and the speed of light are related by the ratio Thus Therefore, the gravitational potential determines not only the speed of light, but also the value of the Planck constant. the greater the absolute value of the gravitational potential, the smaller the value of the Planck constant. This means that at a point with a higher absolute value of the gravitational potential, the quantum uncertainty value is less, and this in turn means that the probability of a particle's transition from a point with a lower gravitational potential is greater than the probability of a particle's transition from a point with a higher gravitational potential to a point with a lower absolute value of the gravitational potential. The Institute of Special Studies (Saint Petersburg, Russia) announced in 2016 that it would pay a prize of 100,000 us dollars to anyone who provides IRREFUTABLE proof that the GRT is correct. The bonus has not yet been paid to anyone and the offer is still valid. -

Experiment verification of General relativity
SergUpstart replied to SergUpstart's topic in Speculations
Unfortunately, I can only give a link to a Russian-language source http://www.vixri.com/d/Janchilin V.L. _Kvantovaja teorija gravitacii.pdf -
I can suggest an experiment to test GRT based on the verification that the speed of light does not depend on the gravitational potential. It is known that the speed of light is a wound The experiment consists of launching two spacecraft from earth. one flies towards the Sun, the other away from the Sun. Each device is equipped with equipment that will accurately measure the value of the magnetic constant and transmit the results of measurements to the earth. If the value of the magnetic constant does not change, then the GRT is correct. If the measured value of the magnetic constant decreases on a vehicle flying towards the Sun, and increases on another vehicle, then the Yanchilin's formula is correct In the link, the results of astrophysical measurements, which can be interpreted as the fact that in the vicinity of massive bodies, the magnetic constant decreases https://science.sciencemag.org/content/358/6368/1299
-
There is another opinion. Not concentration increase in CO2 causes warming, but rather warming increases the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere, due to the fact that the solubility of CO2 in water decreases with increasing temperature, i.e. by heating of the global ocean dissolved CO2 goes into the atmosphere. Perform a simple experiment, pour carbonated water into a glass and heat it slowly.
-
Perfect dark matter are photons. They do not emit anything, do not even Shine with reflected light, and we see a photon only when it hits us in the eye.
-
Yes, you are right, not Yanchinin but Yanchilin. Briefly, the essence of his theory, as it explains the mechanism of gravitational attraction. The square of the speed of light is equal to the gravitational potential with a minus sign Planck's constant and the speed of light are related by the ratio Thus Therefore, the gravitational potential determines not only the speed of light, but also the value of the Planck constant. the greater the absolute value of the gravitational potential, the smaller the value of the Planck constant. This means that at a point with a higher absolute value of the gravitational potential, the quantum uncertainty value is less, and this in turn means that the probability of a particle's transition from a point with a lower gravitational potential is greater than the probability of a particle's transition from a point with a higher gravitational potential to a point with a lower absolute value of the gravitational potential.
-
I expressed this idea ( that the square of the speed of light is equal to the gravitational potential) on another forum and received the answer "This idea is not new, on its basis V. Yanchinin developed the quantum theory of gravity". You wrote that you know several languages, including Russian? If so, here is a link where you can read this theory. http://www.vixri.com/d/Janchilin V.L. _Kvantovaja teorija gravitacii.pdf the Theory is very interesting and very likely correct.
-
Does this mean that if in a static gravitational field you move a body in space from point A to point B along different paths or at different times, the amount of work against the force of gravity can be different?
-
I don't know about the Gulstand-penlevet coordinates, but if we assume that c^2= - Phi (Phi is the gravitational potential), then the formula E=mc^2 transforms into E= - m*Phi with an understandable physical meaning, a body of mass m has energy that must be applied to move it to infinity, where the gravitational potential is 0. This is just information to think about
-
You probably just forgot to write the word operator after the word vector. In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of the outward flux of a vector field from an infinitesimal volume around a given point. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Divergence From the point of view of physics (and in a strict sense and in the sense of intuitive physical image of a mathematical operation) the divergence of a vector field is a measure of the extent to which a given point of space (or rather a sufficiently small neighborhood of a point) is a source or a drain of this field: div F>0 — point field is the source; div F<0 — the field point is a drain; div F=0-there are no drains and sources, or they compensate for each other It is quote from the Russian-language version of Wikipedia, the English-language version does not have this https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Дивергенция
-
Let's write Newton's law of universal gravitation in the differential form div g = - G*ro The divergence Operator shows where the field has a drain and where it has a source. If the divergence is positive at a given point in space, it means that the source of the field is there, and if it is negative, then the flow of the field is there.From the above equation, it follows that the gravitational field has only drains. Where are the origins? in infinity? But then gravity must propagate at an infinite speed, which is not true. So where is the origin of the gravitational field?
-
The electromagnetic field with its mass and momentum creates gravity, which changes the direction of movement of electromagnetic waves. In this case, gravity is an additional source of gravity or anti-gravity. I'm leaning toward the latter.
-
NASA researchers conducted experiments in Antarctica and found evidence that a parallel universe, like our own, was formed as a result of the Big Bang. https://www.forbes.com/sites/jamiecartereurope/2020/05/21/has-nasa-found-a-parallel-universe-where-time-flows-backwards-the-truth-behind-the-headlines/#211c18e0646d NASA researchers discovered high-energy neutrinos in Antarctica that were moving away from the center of the earth into space. This should not happen because high energy neutrinos that came from space from the other side of the earth should be absorbed in the earth's core. But since they were discovered, it was concluded that they came from a parallel universe and time for these particles goes in the direction opposite to the flow of our time. And if you look for another explanation for this, a more mundane one. For example, it has been repeatedly reported that the glaciers of Antarctica are melting under the action of geothermal heat from a tectonic fault. http://www.plateclimatology.com/west-antarctic-ice-sheet-melting-from-geothermal-heat-not-global-warming We can assume that under Antarctica, close to the surface of the earth, there are nuclear reactions that are the source of these high-energy neutrinos, and then the eruption of a supervolcano should be expected more likely in Antarctica, and not in Sumatra or Yellowstone national Park