Everything posted by Pbob
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
I have only just joined this forum looking for help . You mentioned the strong nuclear force isn't electrostatic , then what is it ? Is it a negative energy force between protons and electrons ? Is the proton actually a negative energy and the electron a positive energy ? -ve*-ve = F What is this force ? I understand in algebra that a is not neccesarily proportional to b . I assume the Higgs field can't be a monopole and must be a+b Sorry for the bold , can't get it remove .
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
It equals 0 net charge , not 0 mass . -1e +1e = 0Q = m1 In algebra a+b = 1 Help me please , consider an atom -1e + 1e = 1 atom How to explain the strong nuclear force better rather than using charge ?
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
I have a model and evidence so please do not close the thread I will try to workout how to upload the model . I have already given evidence in the fact that light accelerates when exiting a medium . Here is a 3 dimensional matrix of gravitational transition force and 1ev (photon energy) divided by gravitational transition force in the smallest 3D volume possible .
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
How do you know it is not ? The Higgs field is stated as an energy field that occupies all of space , it is not stated what the components of this field are . As you know a monopole cannot exist without containment . A Higgs field would have to have a binding component such as the atoms strong nuclear force . The closest we are is C/V which might as well be m/V density . I am listening to the right direction .
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
Tit for tat , or you are underestimating my advanced understanding on certain process's . The speed of light is zero , the speed light is attracted to lesser energy spatial regions is c . The gravitaional transition force is the consequence of light momentum , proven by Newtons first law of motion and light passing through a medium accelerating when exiting the medium .
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
Pardon ? How can you derive d/t without an exact measure ? How can an equation explain a speed without an actual measure ? Secondly I am not making stuff up , the argument I presented is being ignored and is actual physics . Why does light accelerate back to c when exiting a medium ? Newtons first law can't apply or the light would exit the medium and not accelerate . F=ma , mass times acceleration, this implies lights acceleration exiting a medium is an act of force . Are you going to ignore this evidence ?
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
The point in continuing is to help to discover the maths . If I didn't need help I wouldn't of bothered with a forum to begin with . If -1e+1e=1 is the properties of a Higgs field and singularity that is expanding , wouldn't it be nice to describe this field between us all in maths or formula terms ? You said C/m^3 which is fine for interior kE but what about the origin ? C/? please tell me what an unkown volume would be ?
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
Your opinion is incorrect , all heat can be observed using thermal observation equipment , heat energy is light and has density . The denser the light , the darker in observation it becomes . Observable black light is when light is at its densest form . Have you heard the term spectral transitions before ? It is natural for any high energy state to disperse energy to lower energy states . The gravitational transition force is responsible for all natural motion in the universe , I am aware you are not familiar with this term but I assure you that a body in motion that temporal conserves energy , conserves momentum . Bodies orbit because they are attracted to the space ahead which is a lesser energy state than the body , the body conserves energy that makes the transition with the body . Light is attracted to any region or point of space that is in a state of less energy . I don't see your link sorry but light slows down passing through glass because of the permitivity and permeability of the glass . It travels through the glass because it is been pulled through the glass by beyond the glass which has less energy in the space than the glass .
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
''an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.'' Proof : Light passing through a medium slows down but once exiting the medium ,speeds back up to c . Light exiting the medium cannot physically speed up unless there is applied force . Light leaving the medium could not speed up and push the light ahead back to c without accelerating . The only way light can accelerate to c when leaving a medium is if it is being pulled by a constant force . Newtons first law fails when light slows down in a medium and speeds back up again on exit of the medium , it is not an explanation of lights momentum .
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
If it is cold outside and I turn up my central heating , there is an increased exothermic process from my house . This is called the transition of energy , high energy states naturally transition to lower energy states . When you turn on a light switch and the bulb lights , the high energy of the filament makes a transition to the room space . The transition force is the force I am looking to explain . Lesser energy states applying a force on high energy states . There is no mistake in considering that a negative of energy applies an attractive force on energy . Formulas work with the physics , I am not trying to make up a formula , I am trying to discuss a formula and looking for help with this formula . Velocity is speed and direction , would v(hf) represent the velocity of light ? v(hf) ∝ F(<hf) ?
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
Ok thanks . The speed of light which is c , is a consequence of force . I want to explain this consequence in formula terms rather than just words . We already have the measure and result which is c . We do not have any math why it is c other than d/t=c I want to explain the light speed process in formula which doesn't exist . Light divided by a force , what can we use to describe this ? Anology : I divide a cake by force I am aware F=ma but this force isn't the same force .
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
I see that now thanks . I am trying to describe why light travels at c and it is my opinion it is pulled along by force . Can I descibe hf/F=c ? Where F is an attractive force vector and hf is high frequency photon ? The speed itself ! I think hf/F=c is now correct ? The force value still to be determined .
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
I don't know calculus , I have no idea what your formula represents sorry . In my opinion any sort of Higgs field would be zero density at any point because of the ''negative of energy force'' being applied externally . Mass can only be divided by volume if we know the volume size , I am not sure that helps . If the assumed Higgs field is a form of energy and has mass , the mass would be divided by an unkown volume and if expanding , gain mass . We assume light is a particle or a wave , Einstein said why not both , why not neither ? What if visible light is just electromagnetic fields ? What if the Suns electromagnetic field extends all the way to the Earths surface , converged with the Earths magnetic field ? The Suns electromagnetic field and the Earths eletromagnetic field are observabaly indistinguishable from each other and space . If there is a Higgs field , likewise it is observabably indistinguishable from space and EM fields , it would perhaps have the same components has EM fields . Note : Observable and detection are not the same thing . Do you know what math or symbol would represent an unknown volume of space ? C/? = ? Relating back to Coulombs .
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
How would you describe the same physics except with a massless volume ? HIggs field divided by empty space I am trying to describe in math terms .
-
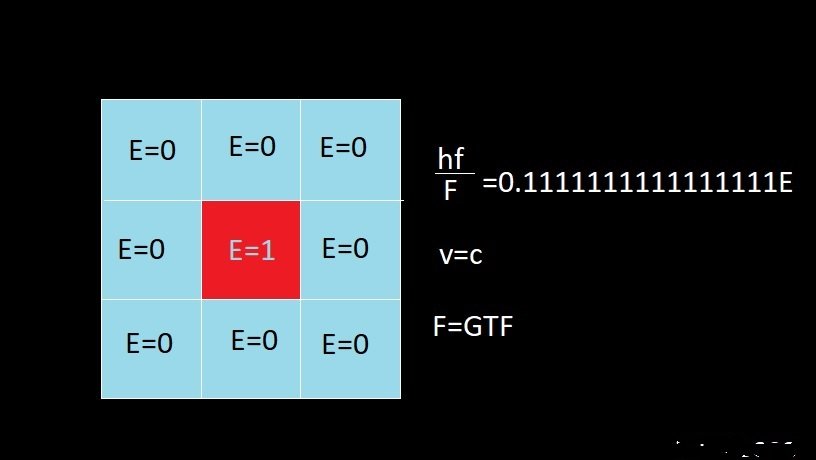
Does this math explain lights speed ?
''A wave function in quantum physics is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The wave function is a complex-valued probability amplitude, and the probabilities for the possible results of measurements made on the system can be derived from it. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters ψ and Ψ (lower-case and capital psi, respectively).'' '' For the case of vacuum (aka free space), ε = ε0.'' I now withdraw the question though , since I have found out ε0 has a value which is incorrect for what I am attempting to explain . What symbol in physics math if any would describe a case for a vacuum , aka free space , negative of energy ? I am trying to explain +/-=c except the neg applies a force . Could I desribe Ψ/F=c ? Where F is force The value of F yet to be determined
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
Considering the Higgs field as a singularity and whole means the consideration of the Big bang singularity . I base a strong nuclear binding force on our present understanding of particle physics . I assume the possible Higgs field must have a strong nuclear binding force because otherwise the 'conservation of form' of the dimensions , would be instantly lost , converted into radiated energy hf/ε0 rather than a progression of form over time . This is my 5th post today , I look forward to more great discussison .
-
Does this math explain lights speed ?
Ψ/ε0=c?
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
Considering the Higgs field as a singularity and whole ''a closed surface S enclosing any volume V, Q is the total charge enclosed within V, and ε0 is the electric constant.'' Would the answer be Q/V then or 1/V ? Would Q/V = 1/V ? Assuming the Higgs field is some sort of nuclear field with a strong nuclear binding force . Would = 0 mass density ? Could the Higgs field have a mass of 1 if it could conserve its density ?
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
'' For the case of vacuum (aka free space), ε = ε0.'' It is my opinion that a possible Higgs field tries to conserve density but is forced to expand by the internal kE production and the possibility of an external force . Opinion based on the possibilty there was never a time when there was an absence of free space . Q could describe a Higgs field if the HIggs field is some sort of nuclear field with a strong nuclear binding force , that works to conserve density .
-
Does Gauss's Law explain a Higgs field and universal inflation ?
''The Higgs field is a field of energy that is thought to exist in every region of the universe. The field is accompanied by a fundamental particle known as the Higgs boson, which is used by the field to continuously interact with other particles, such as the electron.'' ''In physics and electromagnetism, Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem, (or sometimes simply called Gauss's theorem) is a law relating the distribution of electric charge to the resulting electric field. ''