-
Posts
630 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by wolfson
-
Heat packs contain sodium acetate and water. Sodium acetate is good at supercooling. It "freezes" at 130 degrees F or 54 degrees C, but it is happy to exist as a liquid at a much lower temperature and is extremely stable. Clicking the disk has the ability to force a few molecules to the solid state, and the rest of the liquid then rushes to solidify as well. The temperature of the solidifying liquid jumps up to 130 degrees F or 54 degrees C in the process. When you boil the solid you melt it back to the liquid state. You have to completely melt every crystal or the liquid will quickly re-solidify. You can repeat this cycle thousands of times, just as you can freeze and melt water as many times as you like. So snapping the disk causes the crystallization process. The crystallization of a supersaturated sodium acetate solution is an exothermic process (gives out heat). Hope that helped.
-
Making Hydrochloric acid + Halogen Chemistry.
wolfson replied to Runner's topic in Inorganic Chemistry
The water potential know as Kw = the water constant which is 1.0e-14, the concentration of hydrogen ions. You only use the Kw when calculating the pH of bases (OH), Acids are substances that form hydrogen ions so you dont need to include Kw. So the pH is the hydrogen ion concentration, Anti-log pH value gives you the hydrogen ion concentration, i.e if you have 0.0258 M (molarity), of Hydrochloric acid (HCL), then the pH would be, pH = -log(0.0258) = 1.588 = pH 1.588 (strong acid). And if you had a 0.0258 M of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH, Note the OH), then the pH would be, = 0.0258 / 1.0e-14 (Kw) = 2.58e12 then, log(2.58e12) note no - on log, = pH 12.41 (strong base), hope you got that. -
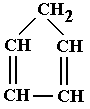
Cycloalkenes can, of course, contain more than one double bond. If there are two bonds then the ene ending of the name is replaced with diene. If there are three bonds then the ene ending of the name is replaced with triene. For more double bonds, the Greek prefix is placed in front of the ene ending to indicate the number of double bonds. An example attached: Cyclopenta-1,3-diene
-
Cycloalkenes can, of course, contain more than one double bond. If there are two bonds then the ene ending of the name is replaced with diene. If there are three bonds then the ene ending of the name is replaced with triene. For more double bonds, the Greek prefix is placed in front of the ene ending to indicate the number of double bonds.
-
Cycloalkanes have all single bonds, cycloalkenes have one or more double bonds and cycloalkynes have one or more triple bonds. (The picture you drew was a aromatic ring). Some examples are cyclopropene, cyclobutene, cyclopentene and cyclohexene, these all have different shapes, cyclohexene is the one with a aromtaic ring (benzene ring). Only the cis-alkene is is possible in cyclic structures with 5 or fewer carbons, trans Cycloheptene has been prepared and exists for a short time before converting to the stable cis-cycloheptene. Cycloalkenes of ring size greater than 7 can exist in both the cis and transforms. Cycloalkenes have the general formula C n H 2n-2.
-
Yes CCCCCCCCC#CCC#CCC#CCCCC(=O)O and H's in appro place.
-
And what are AP's i ask???
-
How weird is that, might be due to a chemical in cigs that react with the copper, it would sure be a aromatic ring. Sweet ciggies lol
-

Making Hydrochloric acid + Halogen Chemistry.
wolfson replied to Runner's topic in Inorganic Chemistry
The Guiness Book of Worls Records in 1957 named these are the top acid (starting strongest first: HClO4, HCl, H2SO4, then HNO3 But i am nearly 100% sure that H(CB11H6Cl6) is the strongest acid at this time. -

Making Hydrochloric acid + Halogen Chemistry.
wolfson replied to Runner's topic in Inorganic Chemistry
The strength of an acid is determined by its degree of dissociation. Complete dissociation of an acid molecule means that all of the H+ (hydrogen ions) are free and able to react. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is one acid that dissociates completely in H20 and is considered one of the strongest acids. Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is often considered stronger because the fumes that it releases are very toxic and it has the ability to dissolve glass, but technically it is a weak acid because it does not dissociate as completely as HCl. -

Making Hydrochloric acid + Halogen Chemistry.
wolfson replied to Runner's topic in Inorganic Chemistry
Well it all depends on molarity (hydrogen ion concentration). 50 molarity (concentration) of HCL would be very stong with a pH of -1.699 -
http://www.stjosephsea.org/library/classification.htm
-
(x-a)(x-b)(x-c) (x-y)(x-z) = x^26 - (Sn PT >>>1 per interval) x^25 The total number of terms in the expansion is 2^26 = 67108864 And the nth term for the un terms would be (geometric progression with a ratio of 2). A(x) = Sum_{n >= 1} a(n)*x^n = x / Product_{n >= 1}(1-(-x)^n)^((-1)^n*a(n) Proof: x prod_{n>0} (1-x^(4n-2))^a(2n-1)/(1-x^n)^a(n). n%4!=2,0,a(n/2)) sum_{k=1.Infinity) B(x^k)/k )
-
Ive got The role of a forensic officer Calculus Physical chem Applied Bio Physics General math Lab rota throughout (analytical)
-
Well the two alcohol's that you just gave are positional isomers, this is where a substituent occupies different positions on the carbon chain. The boiling point of Pro 1 is 370K, and pro 2 is 355K, the boiling points (and other physical properties) of the two compounds are different. Although the chemical properties are the same, the reactivities will be different due to the different envirenments of the OH group.
-
Fats are hydrocarbon chains that either have single bonds (saturated), contain one double bond ([mono]unsaturated), or more than one double bond ([poly]-unsaturated). The [more] [double] bonds that are present, the more [unstable] the molecule, and the more likely that rancidity can occur, releasing [oxygen free radicals that may damage cells]. You got that from my previous post. Alkanes tend to be generally unreactive because the C-H and C-C single bonds are stable and hard to break, unlike the other three bonds (di, tri, quad), the instability increase as the bonds increase, this is due to the energy pushing around the orbitals, more bonds = more energy = weaker bonding = unstable. A way to try and decrease this instability would be to re-direct the orbital energy thus leading to increase bnding ability, far away from doing that at the moment.
-

Do any of you subscribe to Scientific American?
wolfson replied to aommaster's topic in Other Sciences
atinymonkey have you got hang-ups over America? Nationalist do not write Scientific American, scientists write that that magazine, if if your thinking that only "American" scientific magazines contain advertisements on every other page, then you are seriously deluded. And by the way i am not a American, just civil. -
In chemistry we usually call alkanes saturated (no double bond), alkenes unsaturated, and alkynes very unstable and reactive (triple bonds causing this), so as the conectivity decreases (less bonds) the stability increases.
-
Yes you would have named it correctly, this was a functional group illustration, the 6-methyl group was a R donator, the named functional group was only showing the triene group, which is why i only included the triene sample good spot anyway!!!
-
YT look at http://www.noni-juice-distributor.us/nutrition-chart.htm has all about the elements and what they do/help
-
-
Given T1 = 333K, (RH)1 = 75%, and p1 = 1atm. >From this information, at state 1: (p)v = [(p)sat][(RH)1], where (p)sat corresponds to 333K. With (p)v at state 1 and p1 = 1atm, the humidity ratio w1 can readily be calculated. Verify that w1 = 0.01095 If there is no condensation, then w2 = w1.