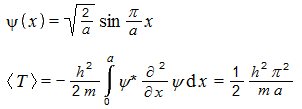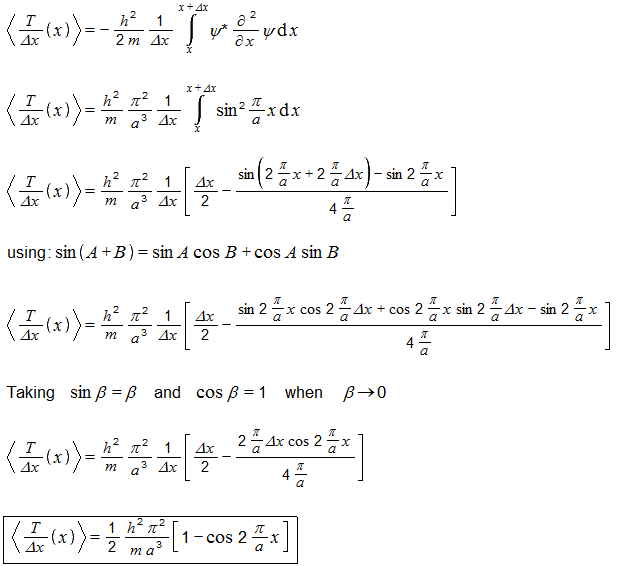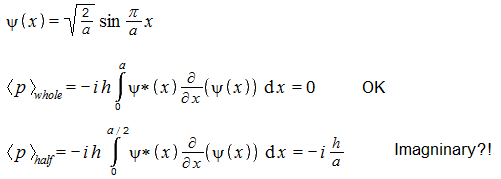Danijel Gorupec
Senior Members-
Posts
716 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
2
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by Danijel Gorupec
-
Beautiful (expressing the g-factor as a ratio of two frequencies where frequencies can be measured very accurately). It does however seem to me that the method assumes certain confidence in equations - that is, that Larmor and cyclotron frequency formulas are both very linear in respect to B. It seems that spin angular momentum of electron is usually obtained indirectly by measuring magnetic moment and assuming that formulas are right. Still, I did find one example where spin seems to be measured more directly - wikipedia calls it Einstein-de Haas effect: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Einstein–de_Haas_effect
-
But this again measures the magnetic moment, no? I don't know how to obtain the g-factor from this data - to obtain the g-factor, shouldn't I also have a direct measurement of the angular momentum?
-
When I ask google how is the spin angular momentum of an electron measured, it points me to the Stern-Gerlach experiment. Yet, I figure, it cannot be the only way... As I understand it, the Stern-Gerlach experiment actually measures spin magnetic moment, but I guess there is some other way to measure the spin more directly - how else would we know the 'g' factor of an electron?
-
Hmm, there are also irrational hopes. I was always worried how could science compete with those guys that promise eternal life. Another thing is spite (or whatever you would call this: "Fu** you and your fu**ing math! Yes, I don't understand it, so what?! I'm not a lesser person! So, fu** you and your damn physics!"? )
-
This is the part that I don't understand... If they asked me, I would tell them exactly the same. You have two sensors, so compare them. Don't make electronics bossy, but assisting.... How come they didn't think of it? I am sure they did - I bet somebody intentionally decided otherwise, and this somebody did not act as an engineer when making the decision. (That said, I think regulatory bodies share the same responsibility in this case as the Boeing.)
-

Particle in a box; 'localized' integrals
Danijel Gorupec replied to Danijel Gorupec's topic in Quantum Theory
This is what I actually wonder - does a quantity obtained that way has any known meaning? For the momentum I obtain imaginary results which suggest it does not have a meaning. For kinetic energy I obtain real result. It might have a meaning. I used this to derive something that seems to me as the 'kinetic energy density' function. But I never heard of such thing before. -
Must every boson mean a force? (Higgs boson too?)
-
Difficult one, but someone might know: At what moment in history are magnitudes of units of electric field (volts per meter) and of magnetic field (tesla) adjusted just right so that we don't need ugly constants in laws like Lorentz law or Faradays law of induction? Was this also the case in dark times before SI units?
-
It might make sense... If the fluid velocity at about 10 meters per second (22mph) and if the magnetic field is 1 tesla (quite strong) then you can have 0.1V per each centimeter of the width of the fluid flow. So I guess if the flow and the magnetic field is wide enough (20-30 centimeters or more) and if other conditions are just right, you can have some electrochemical effect. I however am not very good at chemistry and maybe someone else wants to comment how much voltage is actually needed to start electrolysis (or whatever).
-
If the system is stationary, then no. If the alloy sheet moves relative to magnets, then still probably no. (Any voltage difference that you might achieve with this simple settings seems unlikely to reach some electrolysis threshold - although my knowledge about electrolysis is low.)
-
I heard some amateur astronomers complaining more about bluish light than about reddish light when making observations (I guess, blue disperses more causing more light pollution). I also heard somewhere, but I cannot remember how much was this reliable, that night animals might get disturbed more by bluish light than by reddish light. Anyone heard about this? For me, the ideal street lighting would adjust its intensity during the night - decreasing its power and shifting more red after 23:00h... I guess it might also adjust to foggy conditions somehow... or even to moonlight intensity.
-

Particle in a box; 'localized' integrals
Danijel Gorupec replied to Danijel Gorupec's topic in Quantum Theory
Hmm... but let's compute expectation value for kinetic energy... I am doing this for the same wave-function (ground state particle-in-a-box): ('h' is actually h-bar) The above is the correct result when the integral is computed over the whole box. But even if I integrate over only a part of the box, I still obtain real values - does it mean that such result might have some actual meaning? Not being lazy, I tried to compute kinetic energy distribution (or density) over the box. Moderators can move this to the speculation forum. I am using a sloppy notation as I know no better. This is the kinetic energy density function for a ground-state particle in a 1D box, how I calculated it.... Can this have any meaning? The function shape resembles the position probability density function for the particle. I would be very glad if there is any function that can show kinetic energy density for wave-like particles. I like energy distributed in space (that is, local i like the local conservation of it). However, I never heard anything about it. -

Particle in a box; 'localized' integrals
Danijel Gorupec replied to Danijel Gorupec's topic in Quantum Theory
So, from various sources this is an time-independent wave-function for a ground state particle in an infinite square (widht 'a'). The momentum calculation gives zero, as expected. But if I only integrate over half of the box width (the last line) then I get an imaginary result. Does this mean that this result has no interpretation (that it, it means nothing)? [sorry, the 'h' should actually be h-bar, but I don't have this symbol] -
Hello... Say there is a particle in a 1D box. The particle is in certain state. I know its position-space wave function. I can compute expectation value of its momentum by sandwiching the momentum operator between psi* and psi and integrating over the whole box width (or over whole infinity). Question... If I don't integrate over the whole box, but only over a part of the box, can the result be interpreted as follows: if I simultaneously measure momentum and position of identically prepared setups, and if I only consider those cases where a particle was found within the part of the box for which I computed the integral, then the average momentum of those particles will equal to my integral?
-
Yes, it makes sense to me too... In fact, I guess that the spin-flipping due to the thermal agitation is the reason why paramagnetic materials stop being paramagnetic when removed from an external field. In the meantime I tried to find more argon data to check if argon energy levels are spaced close enough to be excited by room-temperature collisions... unsuccessfully... But I guess not. Anyway, it is my 500th post, and I am giving +1 to everybody... you lucky devils!
-
I understand... I abandoned the idea that rotation of atoms can be used as energy storage (to aid heat capacity). I can accept that atom rotation is not a thing. I am investigating now if electron energy transitions in some heavier atoms are small enough to count as 'unfrozen' degrees of freedom for heat storage.
-
Ok, I see that the 'rotating atom' is a problematic idea. Some back of the envelope calculations, if I did it correctly: Average kinetic energy of a gas particle at 300K is about 0.04eV; The 1420MHz photon has about 6 micro-eV. Therefore, the thermal motion cannot excite an electron in a hydrogen atom from 1S to 2S, but it should be able to flip-flop its spin easily. Is this happening in a real gas? (I guess it might be happening in monatomic hydrogen, but not sure about H2 - probably spin cannot be flipped in H2?) Next, if we are dealing with heavier atoms (say argon) then I expect external electrons have smaller difference between energy levels - possibly comparable to 0.04eV. Should I then expect that those electrons in argon contribute to the heat capacity of argon gas? I guess you are referring to the very high (10.2eV) temperature needed - not that there is some other limitation why collisions are unable to excite quantum states?
-
Hmm... I guess, one way to know that they are rotating is by measuring heat capacity of the gas (and from this we know that they are NOT rotating). But this is a proof of neither, imo. Because atoms are not solid bodies, I guess that their rotation would mean a net non-zero rotation of all the parts. So, when thinking about your last sentence, I guess that my question should actually be: why in monatomic gases, thermal excitation do not cause change in orbital momentum of atom's external electrons? Is this a better way to ask? (I really am not sure what I am talking about - I am just learning the new stuff here).
-
in monatomic gases, why isn't atom rotation taken as one possible degree of freedom - that is, why energy cannot be stored in atom rotation? Is this degree of freedom non-existent or just frozen? Google finds many answers, but they seem to differ. Some say that rotation is simply not physical (whatever it means), some say that a single quantum of rotational energy is much larger than available energy at normal temperatures...
-

Effects of low voltage on an induction motor.
Danijel Gorupec replied to Callipygous's topic in Engineering
I tried to sketch motor torque curves (at nominal and reduced voltage) and some hypothetical load torque curve (a constant-torque load - red line in the graph). You can see how, with reduced motor voltage, the motor will settle at lower speed (lower rpm). This means that its slip increases (the slip says how much its speed is reduced in comparison to the synchronous speed). The thing is that the current the motor draws (its impedance, if you want) very much depends on the slip. As a result, at the reduced voltage the motor will draw significantly more current (It might go above its nominal current causing overheating and stuff, despite the fact that the delivered torque is still at the motor nominal level). As you can understand, some load curves (like that of a fan) will not cause so much problems with a decreased voltage as some other load curves might (the displayed constant-load curve is a bad one). -

How do concentrations of dark matter arise?
Danijel Gorupec replied to Eise's topic in Astronomy and Cosmology
In fact... I am not sure electromagnetic interaction is responsible for collisions in a (fermionic) gas. -

How do concentrations of dark matter arise?
Danijel Gorupec replied to Eise's topic in Astronomy and Cosmology
Hmm... But if they are fermions, they should be, in a way, colliding, no? On the other hand, if they are bosons, they should be lumping toghether, no? I mean, they should be interacting by some mean... unless you believe they are so much different that are beyond wave mechanics? -

How do concentrations of dark matter arise?
Danijel Gorupec replied to Eise's topic in Astronomy and Cosmology
How you described those 'slingshots' reminds me on evaporative cooling - is that how you imagine it? Or you thinking about slingshots caused by massive ordinary-mater objects? (I like to think about DM as gas... I guess, DM particles may still obey Bolltzman distribution of their energies, unless maybe the gas is so cold that quantum effect could prevail... If I suppose Boltzman distribution, then some particles should obtain escape velocity... I wonder if we know the upper limit for the mass of one DM particle?)