TriggerGrinn
Senior Members-
Posts
154 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by TriggerGrinn
-
First I must express what I think is getting close to being the fundamental equation, and would assumably be the concept of 1:1 that I explained earlier. (Mass=Matter) We take E=MC^2 We express it as E / M = d^2 / t^2 (that is Energy / Mass = distance squared / time squared) E / M = d^2 / t^2 The left side of this equation (E / M) is the property of existence. This is, mass and energy Things we refer to as 'tangible' or let us say cause. We will call this "real". It can be a frame of reference. This is SR (scientifically real). The right side of this equation (d^2 / t^2) is the observed part of existence. This is things like, events, change, distance, time, space. These are not tangible, also let us call it effect. This is SU (scientifically Unreal) What has been described above for the perspective of this theory of relativity, in other words the scientific perspective, but NOT our everyday human perception. However on the other hand lets look at this from our 'current' human perception of reality in everyday living. E / M = d^2 / t^2 The left side of this equation (E / M) is Percieved Unreal. We can NOT literally see the mass, and the energy. IE an atom and a photon. It is like magnetics and electromagetics and electrons. These things are elusive. This is PU (percieved unreal) The right side of this equation (d^2 / t^2) is Percieved as REAL. We observe distance or space. We observe change or time. This is what makes up our reality and our existence. If we have space and we have change we have our universe. This is PR (percived real) Now with that said we can begin to see there is form of perception.
-
It may be hard to see what this is saying, so I will paste a post I made that tried to describe this very thing. ___There is still space and time (perceived) in an observation frame. It is just the idea of far away and distant are not really there, you only see an image, or percieve they are there. -however this does not imply that what you percieve can not kill you- An atom for example (or a rock) does not percieve an image of what surrounds it or anything of that matter, Thus it experiences only which contacts it DIRECTLY. Its frame is of zero dimension. Mass and Energy are frames of reference and they are dimensionless. Yes, so it is very possible to assume, in respect to this view on relativity you could eliminate (in your perceptoin) all the space (since it is not there), and all the time (rate of change, since it is not there) in the universe, which would of course UNITE everything that there is, inside one source. This would be a world of mass and energy with no space and no time (no dimension), which is a world we dont directly experience here in the human mind of perception. In respect to this theory it is true we (our consciousness and emotional being of a self) are of this ONE THING (of mass energy) that has NO space in it, and No time in it (like no velocity and restriction of change). However our very human brains and whatever it is that is behind our consciousness (plausibly mass&energy) creates a perception of a world that is infact very illusionary relative to matter and energy. It seems according to this OUR true self of being resides in a dimensionless body of mass-energy, and this human experience creates a perception that you are infact in a universe of grandness, where your percieve dimension. If you take the energy of something lets say a pen, and you devide it by its measured mass. You get a very large number. That number is the speed of light or let us say the measured universal constant squared. So the square root of (the energy of an object devided by its mass) is equal to the constant we see in the universe, that upholds our perception. Energy with the inverse of its mass. So in relation to a very important question in science: What is mass and why does it have the attributes that it has and what is energy and why does it have the attributes that it has? Mass is something that resists events (changing, acceleration) energy seems to resists space (be many places at once). They both have no dimensional quality. Thus To percieve the world of where mass and energy reside, is to percieve one source, of no size and no change. The relationship of space (energy) devided by changing that space (mass) is the fundamental operation behind everything we percieve in the universe. Or let us express it as SQRT(E / M ) = D / T SQRT(E / M ) defines velocity V = D / T Velocity is the universe because velocity is change the universe is change. Change is constant. So there will be a constant velocity, and I presume a constant distance/time, found in this universe. Since D/T represents C. C is found constant, than V=C thus constant velocity Next: SQRT(E / M ) = D / T > The SQRT(E / M ) = C This should relate to this equation in some form. I am not yet familiar how so. Eo , Permittivity = 10^7 / 4*Pie C^2 Uo . Permeability = 4*pie 10^-7 4*pie is the relation ship of a constant of which deals with volume. So We are describing perception (of space and change) with Permeability and Permittivity, thus perception must obey C. So because Permittivity is dependent on C, it shoul be entwined with with energy (light). Permeability on the other hand should define some form of volume for mass.
-
I want to discuss this concept amongst this community. This concept attempts to take relativity that of special relativity to the next step. Please bare with me this time. When Einstien suggested to look at the world without absolute space-time it seemed rediculous to comman sense of newtonian observation. I want to express taking Einstiens space-time and move it to the next rediclous stage to our common sense. Allow me to intro with this. This greatly gives you the perspetive all this is going after. You can detect what is inside your point of observation, then make a perception of what is outside your point of observatoin based on those detections, but that perception is not real, or let us say tangible. You can not grab onto an idea physically. You see, this is describing how our human consciousness Fools us into thinking we are in a NEWTONIAN like 3 dimension spacial entity. Newtonian mechanics http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newtonian_mechanics Which should point to why Newtonian physics fall apart eventually, as it has been measured to do so.
-
I spotted the error. A throws the ball at 15m/s left <--. Relative to B it goes 10m/s. 10m/s @ 10meters = 1second Relative to the ground it goes 10m/s This is actually 10m/s because the destination it reaches is moving away. however that is not all that related. What was concluded here was that both for SR mechanics, and Absolute Relativity mechanics, C can remain constant, on round trip measurments.
-

Project Universe: Build your own scale universe
TriggerGrinn replied to TriggerGrinn's topic in The Lounge
The layer between the oil and the water is flat. Perfectly flat. Whether near the edge or near the center the dropplets remain in static posistion alone. There is no 'pit', nothing like bowling balls on a trampoline. If you add another dropplet they 'want to be together'. I assume these dropplets are of a unique pressure compared to the surrouning layers. More or less, not sure. It was from this experiment that I considered gravity could be directly related to pressure within an aether, Pressure = gravity source. Mass alone does not generate much gravity. Density alone doesnt generate much gravity, mass and density together make pressure, make gravity. Simple basics, but its a possibility. Anyhow, go ahead and try it. -
I have been working with some experiments recently and in the process I found that one experiment is actually ALOT of fun! That is if you enjoy creating your own universe! With working gravity and functioning galaxies. How to build your own function scale universe. Supplies: *1 glass cassarole dish or other type of large flat see-through container (to hold water and cooking oil). *Water *Cooking Oil - the thicker the better, the clearer the better. *An eye dropper or equivelint device. Directions to construction: Place your Glass container on your work station. Proceed to fill the container with cooking oil 1/2 full. (be careful not to shake the cooking oil or disturb it throughout the construction of the mini universe. As it will add to alot of waiting time and uncessary comets! and meteors ) Then Gently fill the Glass container with Cold water. Let everything settle long enough untill there are virtually NO bubbles in the water or oil. Place in the refrigerator to COOL all the fluids as much as you can. (this allows everything to live longer) When you are ready to construct a universe remove the dish from the fridge carefully. Get you eye dropper. Drop small drops of water in your place of choice of the space. Lets call these little chunks of rocks or planets if you will. Scatter them around. if they do not sink try dropping the water dropplets pre-submerged in the oil. The water dropplets will sink down in between the Oil layer and the water layer. The interesting thing is that the dropplets are attracted to eachother, be it electrostatic forces, or gravity itself, that I really dont know. However it acts over very large distances like gravity! So after you have placed some 100 or so dropplets all around the tray let it sit and watch the universe transform before your very EYES!!! galaxies will form at the center of some galaxies large objects will join into large stars with much more powerful sources of 'gravity' Then galaxies will begin to collide and obliverate eachother. Once you get used to this you can mess around with it in anyway you want!! One thing I have done is used a siringe and placed it right near the meeting point of the water and the oil. With proper ejection you can create a massive dropplet. A supermassive black hole! that will gobble up your universe. Please enjoy, and use food coloring if you like to add different colored planets. Notice that overtime many water dropplets will disintigrate back into the main water body source. But I find the colder you keep the liquids the longer everything will play out.
-
It came about because I gave a starting point that said. The first throw took 1second, relative to all observation frames. Because the ball is at a constant, it comes to 10meters.
-
Let me summerize it to make it easier. Rule: ball must travel a distance at 10m/s constant. First: A is moving at 5m/s this way ---> B is at rest. A has the ball o Distance between a and B is 10m just as A throws it. (B)---10m----(oA-->)------------------------------|50M ***** Second: A throws the ball at 15m/s left <--. Relative to B it goes 10m/s. 10m/s @ 10meters = 1second Relative to the ground it goes 10m/s Relative to A it goes 15m/s. 15m/s @ 10meters = 1second It takes 1 second for the ball to reach B. (B)----10m-o--(A-->)------------------------------|50M (Bo)----10m---(A-->)------------------------------|50M ***** Third: B throws the ball at 10m/s , right -->. Relative to B it goes 10m/s. 10m/s @ 50m = 5seconds Relative to the ground it goes 10m/s " " Relative to A it goes 5m/s. 5m/s @ 50meters = 5second It takes 5 seconds for the ball to reach A @ distance 50m. (B)----------o------------------(A-->)---------|50M (B)-------------------------------------(oA-->)|50M Relative to A the ball moved first at 15m/s then at 5m/s and still measured out to be equal with the balls constant, C=10m/s Relative to B the ball moved first at 10m/s then at 10m/s again and measured out to be equal with the balls constant, C=10m/s Relative to the ground the ball moved first at 10m/s then at 10m/s again and measured out to be equal with the balls constant, C=10m/s
-
What I am demonstrating is not yet mentioned. I was wondering if the math work looked good. What do you think?
-
I need someont to check my work. In Absolute Relativity, as you speed up you gain kinetic energy just like in SR. But the Atom will then act in values of greater than C in the direction away from motion. Its like if you run this way ---> at 5m/s and you throw a ball this way <---- you have to throw it at 5m/s make it stop relative to the ground. But lets say the ball is like light and must always travel at the constant. Lets say the constant for the ball is 10m/s. You the thrower needs to throw the ball at 5m/s + 10m/s again to make it travel 10m/s to a person wanting to catch it. Relative to the catcher the ball moves at the constant 10m/s. You can not detect light traveling away from you. We exclude the balls velocity when it leaves you at a hypothetical 15m/s. The catcher catches the ball. he wants to throw it back to you. The ball can not exceed 10m/s relative to the ground. So he throws it at 10m/s. You are traveling 5m/s. The ball slowly gets to you. at 5m/s If you measured the time it took for the ball to go from you to the catcher back to you, it would be 15m/s <--- this way 5m/s this way --> So lets pretend you did a measurement of how long it took the ball to travel from you to the catcher and back. The distance apart at the end is 50m. -The ball traveled 50m to reach you. -at 10m/s - 5m/s = 5m/s relative to you -so it took 5 seconds to reach you from the catcher. -when you through it to the catcher it traveled at 15m/s according to you(10m/s relative to the catcher) -you were running at 5m/s so 5 seconds ago you were 25m closer. -the ball took 1 seconds to reach the catcher when you through it. so at 10m/s * 1s = 10m away when you threw it so relative to you the ball went 15m/s and covered 10M yet took 1 second. So it all took 1 second relative to you and the catcher. catcher says: 10m/s * 1s = 10m then catcher says 10m/s over 50M = 5seconds catcher says: 5s + 1s = 6 seconds in total. It covered 50m + 10M = 60meters at 10m/s ...so still 6 seconds. Lets do relative to you. when you tossed it to the catcher - 15m/s for 10meters = 1s when the catcher tossed it to you - you measured it moving 10m/s - 5m/s = 5m/s. The distance was 50M, the ball took also 5 seconds to reach you and you said it traveled 50m at 5m/s 15m/s and covered 10M yet took 1 second. 5m/s and covered 50M yet took 5 seconds. for a total of 6 seconds to cover 50M with variable velocity. How light speed is measured has been done with 'return' trips. So what if you just said move and you timed how long it took for the ball to travel 60meters at the constant of the ball of 10m/s. Well you end up with 6 seconds. Relative to the ground the ball went 10m/s the whole time. constant. We apply this all to light, and we see that when you time light to see its velocity in a round trip you get C. However this does not mean that relative to you it is actually moving C.
-
The theory includes 'time dilation' Just not in the dimensional sense. more of the delay type. Dont get me wrong. I respect the engineers and scientists that have developed such precise data. It is amazing what those people can do. I would not dare to question todays credibility. What I am saying is that because SR has been tested so well, AR must explain the same phenominas, and it does, but it does it with Absolute rest of space. Shaky numbers: I am talking about certain past experiments that added support to SR. like Small time dilations in the billionths of a second. That is admitably a very short time. If you could measure the effects up to 2 full seconds wouldnt you be interested? This would be expensive however, because I am suggesting a detector placed as far out as the moon, on the moon, or orbiting the moon. A more likely scenario would be something like a 1000meter path, which still gives much more credible measurements. Plus the fact that a return path measurement can cancle out or nearly cancle out the effects in an aether enviroment, cause the experiment to be even lesser accurate. A one way path and this configuration adds time, and better detection of change. I'd personally just like to see it happen, mainly because I have come to a conclusion there is a possible option.
-
I mentioned it in simplistic form. You could add a million angles if that was your desire. However, in the most basic form you need two angles at 90 degrees. You measure any time delay or frequency shift. You then rotate the entire setup 90 degrees and test again. Then rotate 90 degrees and test again, and again, and once more for good luck. Then you have a much much more accurate and error free, controversal free test of such effect of aether wind. As I have explained at first glance you can not tell the theory of Absolute Relativity from Special Relativity, they are that similar. They also support eachother. The work in SR can be directly applied to AR. Because they are that similar it would be possible to use either theory to arrive at the understandings we do today. Thus it seems kind of unwise to make a conclusion of which of the two is, when you have inconsistent results in the ranges of 3x10^-17 seconds. The thread is so thin that I am only suggesting it needs to be tested. If AR is tested and disproven in the suggested apparatus, we have gained insight into science, and gained more confidence! SR has pretty shaky numbers backing it up, they are of very very small values. Alot of room for error. If AR is tested and proven correct we have gained insight into science and gained confidence in moving forward. The results of this experiment will give the ability to get values of a entire 2 full seconds if that is how you decide to perform the experiment. That should be CONCRETE evidence! to what is fact. In my opinion, considering the mentioned possibilities, I would prefer a more confident and precise experiment. Untill that time comes, and it will, our opinions on the matter are of no importance. Wouldnt YOU want evidence that would convince people more easily? Create MORE support for science? Move us forward? This is how we can do it.
-
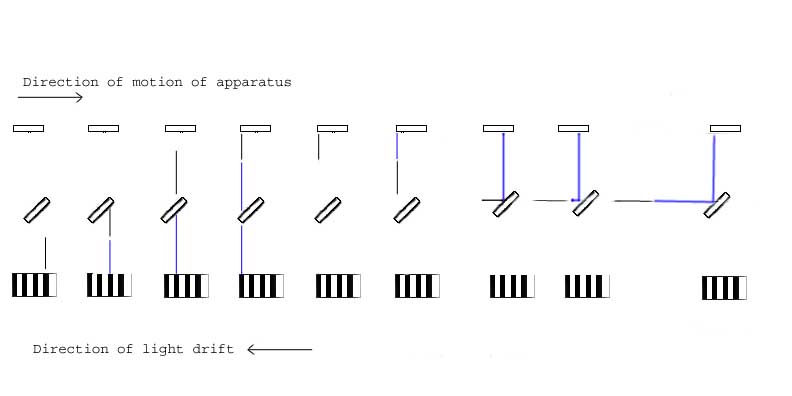
MM experiment expectations in respect of Absolute Relativity. This image shows the path of light through the MM apparatus in the aether enviroment according to the predictions in the AGR theory. The light remains Constant to C realtive to the aether. It aslo remains constant to C relative to any return trip measurements for an observer at rest with the apparatus. As shown, the path time is equal to that C for observer, for aether. There can be no fringe shift as the light paths have equal freqency and arrival time, Just as the MM expirement concluded. A principle that forms under this model is: Light has no momentum. That is, it will not contain or carry the motion of the source it leaves from. Velocity is constant, (no acceleartion). Velocity is proposed to be low enough not to cause too serious of a drift. Just see how the laser(or photon if you prefer) continues in a perfect strait path in the aether at C in 1 dimension (vertical)
-
Agreed. If I can just explain the main part clearly enough then maybe I can get someone's interest, just enough for them to help me speak the language I dont quite get, the physics equations. I just do not have the experience with math to derive equations, flip them around, but I will do what I can and will take corrections when needed. Somebody take a chance on this, hahah, come-on whats to lose. let us go over the Michelson-Morley Experiment. These are the equations and expectations of operation in the experiment. I will explain while refering to this imsage where I beleive it has gone wrong, and what differences come about when you change it (it=the geometry more or less) Note: from this view on the experiment you are like a birds eye view observation frame. This is important to keep in mind. In the 'rest frame' example everything looks great, everything IS right. The only thing to remember is you can not see light travel like this. It is purely a hypothetical diagram to express the visualization. This will become important to understand later in this post. The moving frame diagram is the classical concept of the lights path as it moves with-in a moving frame. It is drawn to cover a longer distance as it reflects along the mirrors. However as I said we are looking from a (birds eye view) observation frame if you will. It is not possible for us to 'see' a photon move along mirrors in this nature. Thus the expectation of it to act in this form is not certain. One would need the light or laser path to reflect off of dust particles (or smoke particles) as it made its journey along the mirror paths. Thus if there is distance between the observer (from our birds eye like view) and the system, then there is a delay in time, and a seperation in posistion in all moving light paths. Let us presume that the light path remains at rest (in respect to the direction of motion of the system) as it leaves the light source. Thus as the light moves along it remains covering the same distance as in in the rest diagram, traveling in a strait line. As the light moves there occurs a very slight drift in the light getting left behind. In this thought experiment, only just a slight drift to cause it to impact the mirror just millimeters the the 'left' in comparison to when it is at rest. Next, the light reflects from this new source, a new photon!, and is sent out towards the center mirror and as it moves it along it again drifts just slightly 'downstream" <--. Lastly, the light reflects from this mirror and is sent from this new source. Again it is a new photon. This source then sends the photon at C relative to the rest, and above C relative system (if we presume we know the velocity of such an aether). The distance the light covered remains exactly the same as when at rest. The velocity of the light relative to at rest never changed. And for any posistion of observation the light would still measure to act at C. An observer that remains at rest with this system observes the same thing, only from a closer distance presuming it is (along for the ride so to speak). Moving onto the fringe shift. The wavelength in the form I suggested would act differently. Laws obeyed: for both the classical form & the form I described -The light would remain at C -The wavelength would change depending on the velocity of the system. (in repsect to observers) In the form I am describing, Once the two different light paths has been 'fired' in the same direction they should then end up as the same frequency one they reach the detect. This is because it is a new photon fired in a new direction and they are both fired in the same direction and the frequency of these two different paths comes from the same source. So on the final aproach they will then regain the same equal frequency. Aswell as the same arrival time. The only shift that could be measured or expected to be measured would be that of experimental error. Let us see results of this experiment. see here http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/relativ/morley.html#c1 or below: We see that there is still a fringe shift. That being two different frequencies arriving at a screen. These shifts are claimed as experimental error. Special Relativity allows NO shift possible. But as you see in the form of observation I have described, also, no shift is possible. Thus if this test is considered to confirm something in science, It has confirmed special relativity, and it has confirmed absolute relativity, since they both would not allow fringe in this experiment. This experiment is not one with alot of confidence. This is why I said there are two techniques to measure light that may give different results. Also, this is why I described the better means of testing for aether.
-
Einstein himself still spoke of a type of ether that was not a “ponderable medium” but something of significance nonetheless. In an address about ether delivered on May 5th, 1920, in the University of Leiden, Einstein had the following to say: “...More careful reflection teaches us, however, that the special theory of relativity does not compel us to deny ether. We may assume the existence of an ether... Recapitulating, we may say that according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an ether... According to the general theory of relativity space without ether is unthinkable; for in such space there not only would be no propagation of light, but also no possibility of existence for standards of space and time (measuring-rods and clocks), nor therefore any space-time intervals in the physical sense. But this ether may not be thought of as endowed with the quality characteristic of ponderable media, as consisting of parts which may be tracked through time. The idea of motion may not be applied to it.”
-
The below is some corrections and editting. Notice in red, typo fixed. You are correct. I can not use an average velocity to assume C, however, let me express just how close a measurement of light in technique #1 (round trip), while the source is moving 0.1C in respect to the proposed aether. Time for light at C to cover 2meters. 6.6667e-6 or 0.0000066667e-6 (seconds) Time for light to cover 1m at 0.9C and another 1m at 1.1C (@ 0.9C) 3.7037e-6 (seconds) + (@ 1.1C) 3.0303e-6 (seconds) = 0.0000067 (seconds) The delay is practically null. However, in the experiment I explained one could get results of much greater accuracy! for example send a signal to a satalite or what have you. eg. Speed of light © to cover 10,000M = 0.033333seconds. aprox. much less room for error. for source to detector experiments.
-
I am not sure I know what you mean by this, but I hope you are not jumping to conclusions. It was an accident that I repeated it and I mean to adress it soon, in respect to the time anyone has spent in reading this paper.
-
yes sir, I do. I That is why I expressed in the paper that the configuration they used is unable to detect any or any significant amount of delay in light time arrival whether or not any kind of aether wind was there or not. Let me research some actual experimental data to further show you want I mean. Question (to anyone): Did you read the re-arrangement of the MM experiment I suggested? That apparatus would be much more capable to test change in light arrival time.
-
I picked up on this last night and was actually quite bothered by it which is why I requested help on that particular section. It is the time average. However I beleive that it there is one small vector additive that should work it out. I excluded it because it was so small. It is for the perpendicular pathways of the light. Of course it doesnt make a difference. I will address it. I just wanted to re-write the paper. I got some corrections to work on. So far I still have not recieved any help in how to write a paper. But I do apreciate the time you all took to review and find errors. thankyou.
-
**rough draft** Need help with this section. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- The Theory of Absolute Relativity Introduction This is a theory of relativity with a form of absolute reference frame. In this paper it is shown that the current laws of physics can still be obeyed by a form of absolute rest (which is hypothesised as an aether). Support is given to this hypothesis by exposing a possible flaw in the original testing for a static reference frame in the famous Michelson-Morely experiment (an experiment that was expected to detect an effect known as an 'aether wind' and more importantly an aether medium). Also, there is a description of the required apparatus to correctly test a form or lack of static medium for light. Furthermore, the paper considers the option of relativity with absolute reference frame (absolute relativity) with relativity without an absolute frame (special relativity) and that shows the indentical simularities between the two theories and what the few differences conclude. Lastly, the list of support for this theory; support from past experiments. The Michelson-Morely experiment In the original Michelson-Morely experiment it was expected to have light wave results similar to that of sound waves or water waves. In the following we see that with or without this expectation the results would remain the same as they were always found to be; No difference in arrival time for two seperate paths of light over the same distance, from the same source, and finally to the same detector. Note: By law of the universal constant of C, light must travel at C relative to each individual observer. If you are not familiar with the Michelson-Morely experiment, Visit this link ( http://galileoandeinstein.physics.virginia.edu/more_stuff/flashlets/mmexpt6.htm ) to become familiar with the apparatus and experiment. Using this program (by increasing the aether speed) you will see a change in the arrival times of the two different photon paths (light paths). These were the expected results that would be found if an aether existed. In the following we show the proposed flaw in the MM experiment. This flaw is that the arrangement of the apparatus is and was unable to detect an aether wind whether it is or was there or not. According to absolute relativity lights velocity can be measured in two techniques. Technique One: Simply send light from a destination (source and considered observation frame) to a destination where it will reflect and return to the source/observer. The time it covers the specific distance in the total round trip journey is measured as the velocity of light. This configuration of measuring the speed of light has been found to be a consistant velocity for light in any direction the pathway of the light was configured. Which is initially expected to support non-absolute space by reason of constant velocity of light. Technique Two. (Note: Principle of Absolute relativity; No observation frame (observer) can detect and/or measure light that is emitted from its frame) Light is sent in a strait A to B path from source to a detector. The clocks for observer and detector have to be previously syncronised. The clocks need to be accurate enough to detect a change in the range of approx. 0.0001 of a second see here: (30km/sec [earths predicted speed] / 300,000km/s [about lights speed] = ) 0.0001. The light must be sent in various directions; a) parrallel to the motion of the apparatus (earths motion); in the same and opposite direction. b) perpendicular to the motion of the apparatus (earths motion), in both perpendicular directions (seperately). Thus once this has been peformed one can conclude the speed of light traveling from a source to a detector (A to B) is consistant with C. (Note: No round trips! the observer must not detect the light that was emitted from its frame. In order to measure the velocity, the clocks between the observer and the destination [detector] must compare actual arrival time [for detector] with calculated arrival time [considering the distance of A to B and the velocity of light] for the observer.) (Note that the MM experiment does not include the form of technique two.) The following is the calculated result of the MM experiment in respect of the two techniques to measure the speed of light: For mathamatical purposes: The system is moving through the aether at a velocity of 0.1C. Velocity(light) = Velocity(source) + C, or V(l) = V(s) + C note: C is speed of light note: Velocity(light) relative to the observer (the system). Also, the Velocity(source) is negetive (-) in upstream aether and remains positive (+) in downstream & perpendicular motion relative to the observer (we exclude a velocity change when the light makes a perpendicular path relative to the system due to the very small change for simplified explanation). Image 1. http://www3.telus.net/hill/MichExperiment.jpg step 1:The light leaves the laser (light source) head on into the aether. The measured and calculated velocity of the photon is 0.9C relative to the source frame (the system 0.1C). In respect to light moving through an absolute medium the movement through such an aether is expected to create a wind effect that would affect the velocity of the light as it made its way through relative to the observer. Light path A & B: V(l) = -V(s) + C V(l) = (-0.1C) + C V(l) = 0.9C Image 2. http://www3.telus.net/hill/MichExperiment2.jpg step 2:The light splits into the two perpendicular paths. The green arrow (we call A) remains going 0.9C, as the paths has been unchanged. The red arrow (we call B) turns perpendicular to the aether and is reflected from the center mirrior at what is now capable to travel at C or 1C. Light path A: V(l) = -V(s) + C V(l) = (-0.1C) + C V(l) = 0.9C Light path B: V(l) = V(s) + C V(l) = (0.1 C) + C V(l) = 1.1C Image 3. http://www3.telus.net/hill/MichExperiment3.jpg step 3:The light reflects from the outter most mirrors (of equal distance from center) and returns to the center mirror. Light path A: V(l) = V(s) + C V(l) = (0.1C) + C V(l) = 1.1C Light path B: V(l) = V(s) + C V(l) = (0) + C V(l) = 1C Image4. http://www3.telus.net/hill/MichExperiment4.jpg The light path A reflects from the mirror and turns pependicular to the system on the final stretch to make there way to the detector. note: one arrow was crossed out to show that they have returned to one wave form again. Light path B passes unchanged through the half silvered mirror (center mirror) and continues on its way to the detector. Light path A: V(l) = V(s) + C V(l) = (0) + C V(l) = 1C Light path B: V(l) = V(s) + C V(l) = (0) + C V(l) = 1C Image5. http://www3.telus.net/hill/MichExperiment5.jpg This table shows the different velocities of the light relative the experiment system in each step and direction. We see in the table that although the velocities changed in one way directions, they cancle out as 1C. 0.9C + 1.1C = 2C. The average is 1C. Or the "return trip" would result in C. note:(unable to show this step where 0.9 one way and 1.1 the other equates as equal to the time of C for both ways: help?) However, when we look at the velocity of the light relative to the aether (absolute frame) through each path and step we get. Velocity(light relative to aether) = Velocity(light relative to source) + Velocity(system/observer) note: towards source is negetive (-) and towards or perpendicular remains positive for Velocity(light relative to source) Equation flip: Velocity(light relative to source) + Velocity(system/observer) = Velocity(light relative to aether) path A step a)0.9 + 0.1 = 1 b)0.9 + 0.1 = 1 c)1.1 - 0.1 = 1 d)1 + 0 = 1 (we see in path A of light, it remained C at all times relative to the aether, and C relative to the observer [when it returned]) path B: step a)0.9 + 0.1 = 1 b)1 + 0 = 1 c)1 + 0 = 1 d)1 + 0 = 1 (we see in path B of light, it remained C at all times relative to the aether, and C relative to the observer for return trip measurment. Thus the velocity of light in conventional measurement obey's the constant speed of light for both aether and observer. How to correctly detect a form of aether. If Michelson-Morely Experiment was rearranged in the following configuration an result could be found in an aether enviroment. An example of the corrected appartus. Note: light sources aimed in perpendicular angles laser (light source 1a) to ------------> detector (1b) @ angle x laser (light source) (2a) to ------------> detector (2b) @ angle y The prediction of this theory is that the result would find: - a difference in arrival time for the two light sources - a difference in frequencies between the two lights (if their sources were identical - a velocity of the aether This is a general simple form of the experiment. If the light was capable to make a return trip the experiment would fail to show any change between the two light paths and light would be measured to be a constant of C. The light must make one path from A to B to detect any change with aether effects being hypothesised. Special Relativity with Hypothesised Absolute Relativity. The following list is the simularities and differences between the theories and the consequences. Simularities Special Relativity: - Special principle of relativity - The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference. In other words, there are no privileged inertial frames of reference. - Invariance of c - The speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant © which is independent of the motion of the light source. -proved true or false by measuring the constant speed of light in both mentioned techniques in all directions. Absolute Relativity: - Special principle of relativity - The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference. In other words, there are no privileged inertial frames of reference. - Invariance of c - The speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant © which is independent of the motion of the light source (with return trip measurments). -proved true or false by measuring the constant speed of light in both mentioned techniques in all directions. Differences: Special Relativity: -No stationary reference frame -distance and time depend on the observer, and that time and space are perceived differently, depending on the observer. (space-time). -no properties of aether Absolute Relativity: -stationary reference frame -distance and time is fixed: Time has two explainations. 1)That what light shows and the rate of which it is seen within an observation frame 2)A constant fixed time among all material in the universe in syncronization. Distance and posistion of objects is uncertain at relativistic velocities. That is the posistion of the object relative to the observed light is not the same, thus the object is equal (=) time (t) in the future to the observer as is the time in which it takes the light to reach the observer over the specific distance, and futhermore is also dependent on the objects velocity relative to the observer. -properties of aether are that light can only be made into its wave form at the velocity of C which is determined by the permittivity and permeability of that space. The atom as freedom to act up to the velocity of C relative to the aether. Eg. If an object was moving at 0.9C through space it would be capable act in 0.9C + C away from the direction of travel, and 0.1C in the direction of travel. The propose element here is that this is the reasoning behind E=MC^2. The concluding accertion: The hypothesised result of these simularites and differences is that all observed experimental data can be explained in two options; Special Relativity and Absolute Relativity. The explainations to specific experiments is not yet included in this paper. It is possible for medium (aether) like universe to obey the laws of physics and create the same experimental observation that have been performed to test the theory of SR with space-time mechanics. Support on this theory from past experiments In my research I came across an experiment in the past that found a change in the frequency of light emitted from a gas that was excited by a source of light. The source of light and gas was placed on a turntable in which it could change directions relative to space as it did a change in wavelength occured. The following are the links of which support this claim. http://www.wbabin.net/physics/kingston.htm The Mössbauer effect Check near Fig 4 (below Enter Mossbauer) http://www.rsc.org/Education/EiC/issues/2002July/july2002Adetunji.asp apparatus image. - http://www.rsc.org/images/adetunji_jul02_fig4_tcm18-36458.jpg The angle of light source propogation in respect to space can directly affect the frequency emitted from a gas that is excited by the same light (energy) source.
-
I will address it. I'd like to hear your thoughts after. The details so we can decipher whether or not we are on the same page. -The MM experiment was setup to test for aether wind. -The experimenters configured it to detect a difference in arrival time for two different paths of light. -Over many years no change was ever detected. -Every experiment that successfully tested the speed of light very accurately involved sending light to a destination, then, reflecting it back to a detector. This configuration found a consistant velocity for light in any direction the pathway of the light was configured. -No observation frame can detect and/or measure light that is emitted from its frame. However, if the light is sent to a detector where the clocks are in syncronization and those clocks are accurate enough to detect a change in the range of (30km/sec [earths predicted speed] / 300,000km/s [about lights speed] = ) 0.0001. This is the range of the best scenario of detectable results, presuming the path of the light is in parrallel with the direction of travel of the experiment.Once that has been performed, one can conclude the speed of light traveling from a source to a detector (A to B) is consistant with C. -Any light that makes a return trip will measure to be C with or without including the possibility of aether. Although, even if aether is presumed, a return trip will measure to cover distance/time = to C. If we agree to be on the same page with that all laid out, we can begin to look at the MM experiment and apply these principles. The MM experiment sends light in parralell aswell as perpendicular directions from the source. -Note that even if there was motion through an aether medium it would Cover each of the two paths in the same amount of time (considering they are equal in distance). -Note also that in the aether model light was not expected to travel C in all directions relative to an observer. Thus if they calculated it able to travel slower than C upstream (relative to the motion through the proposed medium) then it would be able to gain velocity going downstream (the aether wind) beyond C "RELATIVE TO THE OBSERVER IN ONE DIRECTIONAL PATHS". However, the average of gain in one direction and loss in the other resorts back to C. Vl = (0.1 C) + C Vl = 1.1C and Vl = (-0.1 C) + C Vl = 0.9C Then, 0.9 + 1.1 = 2C/2= 1 = C Or we simply add and subtract motion of system relative to the aether from the measured speed of light. upstream Vl = (0.1 C) + (0.9C) = 1C downstream Vl = (0.1 C) - (1.1C) = 1C which shows that the light never changes velocity relative to its aether. If we compare this to the conclusions of Special relativity. It is the same. Let us call special relativity SR and Absolute relativity AR. SR-The speed of light remains constant to an observers frame. AR-The speed of light remains constant to an observers frame. SR-The velocity of the observation frame is independent of the speed of light when measured. (refer to how light must be measured) AR- The velocity of the observation frame is independent of the speed of light when measured in a return path configuration. Aswell as the velocity relative to the absolute frame -proposed as static space aether-. What does all of this conclude? The MM experiment would be unable to detect a difference in arrival time for light. Thus the results found in the experiment are undefined. There is no certain conclusion. Furthermore, The difference in Absolute relativity and Special relativity is very slim. In fact the calculations continually work out the same. So if we agree either theory or perspective can act in practically an indentical way which one is in fact correct? The only way to tell is to perform the experiment Mentioned in the testing of the theory of absolute relativity. which is: Note: light sources aimed in perpendicular angles laser (light source 1a) to ------------> detector (1b) @ angle x laser (light source) (2a) to ------------> detector (2b) @ angle y The prediction of this theory is that the result would find: - a difference in arrival time for the two light sources - a difference in frequencies between the two lights (if their sources were identical - a velocity of the aether
-
Could you also show your work in what you refer to? I dont know exactly what you mean there. Observer? frame?
-
that meaning the letters and stuff like V' or Vo Vk and things of that sort. I am looking around on the net for such things. I have made my own as you have seen but I would rather have ones I could show that have been and can be derived into what I am trying to show.
-
absolutely. Again, I suppose I have been assumming you would 'put it together' persay, since it is rather simple math. I agree, when put down as a paper, each step must be shown clearly, concisely, and correctly. I dont know the 'exact' official formulas. Instead of getting as you said (hard to be nice), could anyone just offer some formulas and structure? You have not disproven the foundation the theory stands on, the theory has not been disproven. That being the testing of frame A to B light speed tests. I should quit replying with these summerized vague, more verbal type of replies, while I am in the process of laying out the whole layout of the mathamatics.
-
I mean from perpendicular angles. You cant 'imagine' seeing light move like a laser as it passes by. You can not just guess that what you see is where it is. Calculations must be used, and even still the object that the light is coming from is 'in out unknown future' therefore it can not be a certain prediction.