-
Posts
38 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by BeuysVonTelekraft
-

Comprehensive Mathematics for Computer Scientists 1
BeuysVonTelekraft replied to BeuysVonTelekraft's topic in Mathematics
Yay! You answered it! Thank you. So I just need to understand the implications of the axioms and theorems? Now it's kinda easier, I thought I ought to memorize. -
Guys, what you think about: -For dummies books; -DeMYSTiFied books; -Complete idiots guide.
-
Ok, thanks for the advices. I kinda figured the way it should be done (tried?), Algebra, Calculus, then Analysis. I've got some books and I'm gonna start to read them. Thank you so much.
-
The course i'll make starts with Linear Algebra.
-
Hi, next year i'll start my bachelor's degree on mathematics, but i want to study something about it while i'm idle. I've found this: http://webdocs.registrar.fas.harvard.edu/courses/Mathematics.html And this: http://www.ufpe.br/proacad/images/cursos_ufpe/matematica_bacharelado_perfil_4904.pdf They're Syllabi from some mathematics courses, one of them is from the university near me, the other is from Harvard. Can someone suggest a study way? Where should I start and which books I should get? Thanks in advance.
-
From what I know until now - if i know something until now - the DNA can store information. But i've never read about how much information it is possible to store on it, any sugestion?
-
I am reading it here: http://www.amazon.com/Rubato-Composer-Music-Software-Component-Based/dp/3642001475
-
So, if there are lots of possible operations. How will i know what operation should i do?
-
I'm kinda doing what you're doing, i've been negligent with my classes while younger, now i want to build some projects that need the neglected content. I'm reading mathematics for the nonmathematician. It's a cool book if want some maths.
-
Oh, forget, i didn't undertand.
-
I guess the word is not "possible", the word is "known".
-
Can i say: Map it to n, instead of map it to {4,9}? And, where can i find all possible binary operations? I've searched a little but i can't find it.
-
I kinda modeled a monoid on Mathematica: I'm not very sure if i'm right on them. But what would happen in the case of the homomorphism of these monoids?
-
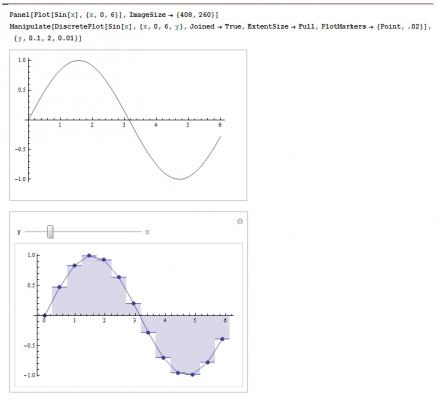
I'm reading Comprehensive Mathematics for Computer Scientists 1, has anyone read it? I've picked this book last year, i wanted to understand the Rubato music composer and after i understood what would be needed to operate it, i asked Guerino Mazzola about a good book to get started on the necessary topics, he suggested me this book. I opened the book and i made the first chapter pretty fast, but when the second chapter came, i swear that the only thing i could see is something like the image below. Now that i know a little more of maths due to books like "for dummies" and "The complete idiot's guide", i open the second chapter and it seems more like the image below: It's russian, it's easy.I can read it slow and stuttering, but i kinda understand it. I have a doubt on how it's reading should proceed. There are lots of axioms, remarks, proofs, sorites, etc. Should i memorize each one of them? What would be a effective way of reading it? Thanks in advance.
-

Suggest some continuous signal
BeuysVonTelekraft replied to BeuysVonTelekraft's topic in Computer Science
Yup, i understand it now, i even did a notebook on Mathematica for the case I need to explain it to someone in the future. The first image is a - theoretically - continuous signal, the second is the discrete signal and the y slider is the quantization level. -
Got it. Now there's another concept on the book: Monoid Homomorphism. Given two monoids [Math] (M, *M)[/Math]and [Math] (N, *N)[/Math], a monoid homomorphism [Math]f : (M, *M) \rightarrow (N, *N)[/Math] is a map of sets [Math] f: M \rightarrow N[/Math] I understand the mapping, and the meaning of the monoid [Math] (M,*)[/Math], but i have no clue of the meaning of [Math](M, *M) [/Math]. The homomorphism, as the name suggests, seems to be making both sets having the same elements, am i right?
-

Suggest some continuous signal
BeuysVonTelekraft replied to BeuysVonTelekraft's topic in Computer Science
Yeah, yeah. I got it. I knew this process of audio conversion, i just didn't know this difference of continuous and discrete. Now it's perfectly clear to me, unless there are some other ill implications on the terms. -

Suggest some continuous signal
BeuysVonTelekraft replied to BeuysVonTelekraft's topic in Computer Science
I wasn't envisioning something specific, i just thought that the natural structure of one object may allow only a finite level of variation on it's properties. I'm also not very sure if i understand what discrete and continuous means, i had a naive definition that, for example, a continuous signal would be a signal that could vary between [math]-\infty [/math] to [math]\infty [/math]. But i've read that when the continuous signal is captured and transformed into discrete signal, it's quantized. This made me think: On a quantized signal, you'll have intervals like 0 - 1, and if you capture say: 0.6 it's gonna be transformed in 1. Now i'm thinking that the continuous signal is the signal that, by not having a quantization, allow [math]\frac{y}{x}[/math] with [math]x[/math] being any number. On a discrete signal, [math]\frac{y}{x}[/math] will be rounded to the nearest interval, instead of being recorded as it is. I was deducting it just now. But thanks for the answer. -

Suggest some continuous signal
BeuysVonTelekraft replied to BeuysVonTelekraft's topic in Computer Science
Oh, analogue signals are the continuous signals. I couldn't think about them because i thougt they had a limit due to natural properties. -
Oh, i got it now. The x in the middle of ZxZ indicates this binary operation is a cartesian product, right? So, this is a binary operation, are there other kinds of binary operations that are not cartesian product? Then, the monoid is something that suggest a operation inside a set, right?Could it suggest only binary operations or is it possible to suggest a n-ary operation? Thanks in advance.
-
I'm reading a book on DSP, and they say that there are discrete and continuous kinds of signals. I can imagine some discrete signals, but i have no idea of what could a continuous signal be. Can you suggest some?
-
I understand now what is a binary operation, now i have a problem with your statement: I've read a definition on wikipedia about cartesian product: And i have this questions: -This kind of mapping make sense to me (the playing cards), but why would I map the elements of the cartesian product SxS to S? -Are there other kinds of binary operation on sets? -Are sets the same thing of lists in programming? I guess so, their nature seems identical. -When he says: (M, *), what's the meaning of *? Thanks in advance.
-
I do understand the concept of set, but not the concept of binary operation.
-
I've searched on wikipedia and wolfram mathworld, and i have a definiton on a book right in front of me: After that there are some properties. But I still can't understand it. Can you help me? Thanks in advance.