-
Posts
18270 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
104
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by studiot
-
Thanks for the replies, from those who managed to find this post. Something else I noticed is missing. Post numbering. In a long thread it is very useful for all concerned to refer back to the post number. So I hope these will return when you have finished making changes Glad to see super/sub script back.
-
Both living and fossil stomatolites are available today.
-
But you are not on an airplane (are you?) Just testing another facility or three
-
You really can't be serious that this is an upgrade for a science site. Where is the list of recent posts? Where is my list of subscribed threads? Why does the users online list umpteen 'guests'. Where are the superscript and subscript? Tex test [math]\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \int {\sqrt {{x^3} - 15{x^2} + 3x - 8} } dx[/math] Why does a popup keep poping up to say 'Do you want to receive notifications from scienceforums ?' when I have already said no 15 times? That is enough for now Edit Well edit works, that I suppose is good Mathml seems also to work (quickly) unlike some forums which is good. Everything appears double spaced, whether I want it that way or not There seems to be no way to post the edit????????????????? Re- Edit You have to use the Edit Topic Button - quite illogical and confusing since I have already pressed edit to get there. Re-Edit 2 Now, of course once I leave it, I have no way to find this thread again to see if there are any replies. The text editor appears more friendly, however. What about reputation points, have these been abandoned?
-
Why are you converting lbs mass if you are talking about thrust? 6000 lbs of thrust (US units) convert to 26700N, the conversion factor is 1lb of thrust is 4.45 Newtons of thrust. https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrust
-
Since the last thread was closed for a total lack of engagement with those offering scientific discourse, I rather hoped you would do the same here following the same action.
-
Thanks Strange, and +1 for finding the correct link, which says that the deflection distance was 0.16 inches, measured to .01 inches with vernier. This seems reasonable as it implies a scale marked on divisions of 0.1 inches divided a further 10 by the vernier. Now it is interesting what this means for the resolution of angle. At a radius of 3 feet or 36 inches 0.01 inches the angle subtended is given by [math]\frac{{\delta \left( \theta \right)}}{{360*60}} = \frac{{.01}}{{2\pi *36}}[/math] Which is approximately 1 minute of arc. (Don't you just love it when things cancel out so neatly) [math]\delta \left( \theta \right) = \frac{{.01*360*60}}{{2\pi *36}} = \frac{6}{{2\pi }} \approx 1[/math]
-
Yes it was inline with what I said. Lining the prisoners up like that is an interesting way of explaining which hat each can see, although it was not put that way in the original. You didn't answer the spinoff questions, why 3 black hats and why is the last person blind?
-
This is a good opportunity for you to understand the experimental method. I think by 'measurement uncertainty' you mean 'measurement resolution'. They are different. So the actual force was very small. Did Cavendish directly observe it? Of course not. He measured something else entirely. This something else was the twisting of a 6 foot beam, against a distance scale. So the effect of the small force was multiplied by a long lever arm. Now another of Newton's Laws asserts that, no matter how small the net force, it will accelerate a body and continue to do so for as long as the net force is obtained. So large effects can arise from small net forces if you wait long enough, which Cavendish did. Note the natural period of swing was about '20 minutes'. So back to the experimental method. Cavendish did not directly observe the force. G and the force were calculated from the data, but not by the formula you quote but by this one (modern version) [math]G = \frac{{\tau \theta {d^2}}}{{Mml}}[/math] Where tau is a previously determined constant of suspension Theta is the deflection angle d is the distance, that you mentioned, between the big and small lead balls M and m are the masses of the lead balls l is the length of the support rod. Now what you need to do, when discussing the experiment is to take that equation and develop the effect of measurement resolutions in each of those quantities, in accordance with the theory of errors. Further in experimental methods it is often known that certain effects change the observed readings and so must be allowed for. In Cavendish's case corrections were applied for:- 1) Each large Sphere also attracted the more distant of the small spheres 2) The attraction of the beam slightly icreases the deflecting couple. 3) The rods supporting the masses also cause attraction. A further experimental technique to increase precision is to take multiple readings and generate some kind of average. Cavendish took 29 readings for his average, but I am not sure of the statistical methods available to him for this calculation.
-
Just to take a very different tack from the current direction of the discussion, back to the thread title. Instinct v consciousness. Many argue in philosophy that our understanding (perhaps not the right word but I am equating this with consciousness) is entirely due to and conditioned by what we sense. Of course we also possess what is called the autonomic nervous system which conditions what we see and our reactions to it. The ground pushes against your feet, but are you conscious of that push? This contradicts the simplistic view that our knowledge that supports our consciousness is what we sense.
-

Calculating the fundamental resonance of an object (not string)
studiot replied to alexr963's topic in Mathematics
Yes it kinda depends upon the shape object, and, as Strange says, the material of the object may cause excessive damping. So a plasticine wine glass will not ring but a glass one can. You are not clear as to the shape, but taking your wine glass example here is an extract from a table of natural frequencies. -
maybe I didn't put it very well, but you have entirely missed the point. Creationists :- The Earth was created as being entirely suitable, yay perfect, for animals and Man. The truth: For 4 billion years the Earth was uninhabitable, yay deadly, to animals and Man.
-
Yes indeed, let's clear up what the wave function is. The momentum px of classical theory is replaced by the operator [math] - \frac{{ih}}{{2\pi }}\frac{{\partial \psi }}{{\partial x}}[/math] and the total energy E of classical theory is replaced by the operator [math] + \frac{{ih}}{{2\pi }}\frac{{\partial \psi }}{{\partial t}}[/math] in quantal theory. The wave function, therefore, is something that vibrates in time and space. The projection or shadow cast by it on the time axis is Energy The projection or shadow on the three axes of space are the three components of momenta.
-
I would say the biggest problem creationists have with fossils is that of the ancient atmosphere, which was totally unbreathable by modern life as it was pretty well devoid of oxygen. The earliest forms of life 'created' the modern oxygen rich atmosphere by photosynthesis, and these lifeforms are still with us today. Stromatolites. ://www.google.co.uk/?gws_rd=ssl#q=stromatolites
-
Yes depending upon the thickness of icing both aircraft weight, lift and drag are affected. This may alter the trim of the aircraft by shifting the four forces mentioned in post#10. Further effects not so far mentioned are that the icing may seize the flaps, landing gear or disrupt the operation of propellor or turbo aircraft. Jets are not so subject to engine disruption. Here is an interesting breakdown. http://www.pilotfriend.com/safe/safety/icing_conditions.htm
-
Sounds good. How about the amount of heat generated per unit time? So work or heat per unit time. And what is the unit of work or heat? Well it is the Joule, since both are forms of energy. and what is the unit of time? The second. So 1 watt is one joule per second. But watts are not energy, we must not forget the per unit time or per second part. Watts are the units of Power which is the time rate of doing work or producing heat. So to remember time how many seconds in one hour? 3600 So if we are working or producing heat at a rate of 1 joule per second we will have produced 1 x 3600 joules in 1 hour. This amount of energy is called the watt-hour. Of course if we multiply everything by 1000 we get So if we are working or producing heat at a rate of 1000 joules per second we will have produced 1000 x 3600 joules in 1 hour. Or to use the kilo prefix So if we are working or producing heat at a rate of 1 kilojoule per second we will have produced 1 x 3600 kilojoules in 1 hour. This is called a kilowatt-hour.
-
Before I answer this please tell me what you think a 'watt' is because a kilowatt is one thousand of them.
-
So which is more attractive Science forums where the rude members ignore you when you put in serious effort on their behalf? or Another glass of single malt? Cheers
-
Yes, indeed the weight of the (displaced) red pointer provides this and is probably the simplest mechanism. +1
-
Just to pick up on CharonY's analysis (which is correct) The point about the the blindness of C is that It doesn't matter what he sees (or doesn't see). What matters is that if he had a red hat on B was in a positon to determine his own hat colour and so C would never have the opportunity to speak. But there are 4 available configurations whereby B can see a black hat on C, so B has to say 'don't know' if C has a black hat. Only once B has spoken I don't know, it becomes C's turn and B will only say 'I don't know' if C has a black hat. Note that for this to happen A can have either a red or a black hat so it is not possible to determine all hat colours from the information given.
-
Yes zapatos has the right approach. Instead of listing all permutations of hat colours, consider the information available at each stage. Information avilable = (what was know before) + ( what can be seen at that stage) So the reason the question is not 2+2 is shown as follows: Assume there are 2 hats of each colour. A goes first and if he can see two hats of the same colour he knows his must be of the opposite colour so he can declare this and terminates the proceedings. B goes second and knows that A cannot have seen two hats of the same colour so since A sees the hats of B and C, B knows this his hat must be of the opposite colour from C. Add the new information B can see the hat of C so knows his own hat must be of the opposite colour from the hat of C. So B declares and terminates the proceedings. So C's declaration is never reached. If you rework the 3 + 2 situation you will reach C
-
Twaddle. Let's be clear. The clever thing that DM noticed and is asking about is what returns the scale to the level position when you remove the load and the weights? Here is one type that doesn't automatically return.
-
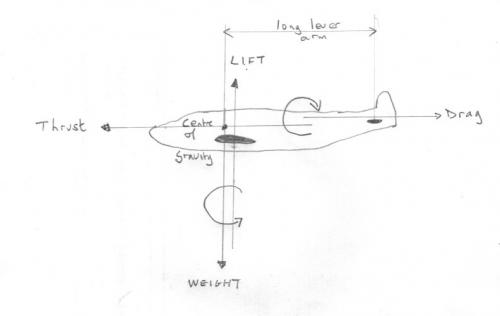
You need to know more than this for your design. There are four basic forces acting on a plane (plus a fifth I will come to). As shown in the diagram they come in pairs and also generate two couples. I have shown the conventionally preferable configuration. The 'Lift behind Weight' couple gives the aircraft a tendency to turn nose downwards in the event of an engine failure so it will enter a downward glide. Lift forward of weight stalls the aircraft's flight. If the drag is above the thrust this counters the first couple to some extent. Both couples can be seen to (preferably) have short lever arms. I have noted a fifth force. This is developed by the tailplane and can be upwards or downwards and can be changed in flight As can be seen it has a long lever arm about the CofG of the aircraft. So a small tailplane can have a large effect. This effect can be used to counter the rotational imbalance between the other two couples. It can also be used to boost the vertical lift force at slow speeds (take off and landing) since the lift is speed dependent. The wingtips in swept back wings can also serve these functions in aircraft without tailplanes. Getting these wrong is the principle reason paper aeroplanes swoop up and stall or drop nose first. Yes check your dynamic similarity modelling characteristics if you wish to scale down full sized wing shapes, as Manticore says. The calculations often result in imparactically high airspeed for the model (several thousands of miles per hour). So some shape adjustment is inevitable.
-
This is my last attempt to hold a conversation. I was going to present this with lots of explanation, but since you never reply I will just present a bald derivation of Schroedinger in one dimension, using Planck, De Broglie, mass and mechanics as appropriate. I shall use standard greek letters except for using f for frequency instead of nu to avoid confusion with v for velocity. The (classical) standard wave equation in one dimension is [math]\frac{{{\partial ^2}\phi }}{{\partial {x^2}}} = \frac{1}{{{v^2}}}\frac{{{\partial ^2}\phi }}{{\partial {t^2}}}[/math] Edit equation corrected. In order to separate the variables write the solution as the product of a function of x and a function of t. Select the function of t to periodically return to zero and be finite everywhere. [math]\phi \left( {x,t} \right) = \psi \left( x \right)\sin \left( {2\pi ft} \right)[/math] Substitution this solution into the original equation yields [math]\frac{{{\partial ^2}\psi }}{{\partial {x^2}}} + 4\frac{{{\pi ^2}{f^2}}}{{{v^2}}}\psi = 0[/math] The total energy of a travelling particle is equal to the sum of its kinetic energy and its potential energy. [math]E = KE + PE = KE + U[/math] and the kinetic energy equals the square of the momentum divided by twice the mass. [math]KE = \frac{{{p^2}}}{{2m}}[/math] Thus [math]E = \frac{{{p^2}}}{{2m}} + U[/math] or [math]p = \sqrt {2m\left( {E - U} \right)} [/math] So substituting into Plancks theory [math]\lambda = \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{{\sqrt {2m\left( {E - U} \right)} }}[/math] But the wavelength is also equal to [math]\lambda = \frac{v}{f}[/math] So substituting into the separated original wave equation [math]\frac{{{\partial ^2}\psi }}{{\partial {x^2}}} + \frac{{8{\pi ^2}m}}{{{h^2}}}\left( {E - U} \right)\psi = 0[/math] Which is Schroedinger's equation in one dimension.